Projects/Usability/HIG/Layout/NavigationPatterns: Difference between revisions
Appearance
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Purpose== | ==Purpose== | ||
Navigation Patterns are determined by the | Navigation Patterns are determined by the structure of the application content. Navigation patterns can be combined with [[User:Andrew/LayoutPatterns/CommandPatterns|command patterns]] to design the complete layout for your application. | ||
==Guidelines== | ==Guidelines== | ||
Revision as of 21:05, 21 July 2014
Purpose
Navigation Patterns are determined by the structure of the application content. Navigation patterns can be combined with command patterns to design the complete layout for your application.
Guidelines
Patterns for a flat information structure
When there is no hierarchical relationship between pieces of content the information structure is flat. Examples include a playlist, a slideshow or a list of documents or contacts.
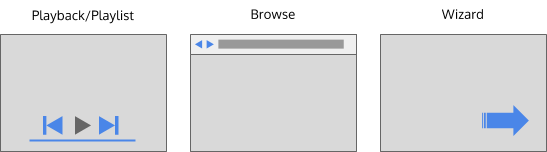
One at a time
- These patterns are useful when each piece of content is meant to be shown one at a time.
- Controls are provided to allow the user to move from one piece of content to the next.
- Examples include a slideshow, or a video or music playlist, a web browser or setup for newly installed software
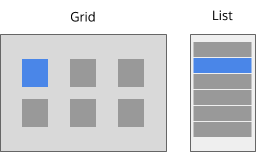
Multiple at once
- These patterns are useful when multiple pieces of content are intended to be shown at once.
- All essential information about each piece of content is visible or accessible within the pattern without changing layout. * If more space is needed to show the details of a selected piece of content consider the Master-Detail patterns.
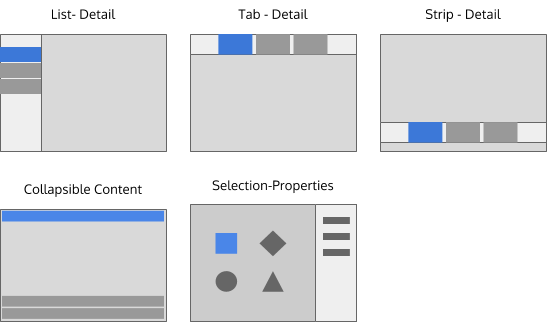
Master-Detail
- These patterns are useful when multiple pieces of content are intended to be shown at once along with a more complete presentation of the information contained in the currently selected piece of content.
- Examples include a contact list that shows the full details of the contact when selected, or a slideshow with the "film-strip" to select other photographs.
Patterns for a 2-deep information structure
When all pieces of application content can be grouped into top-level categories, the information structure is 2-deep. Examples include picture albums, music albums, an email folder or tags.
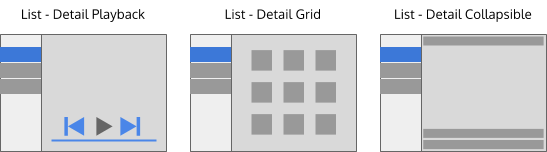
Combined patterns
- Any flat navigation pattern could be combined to create a 2-deep navigation patterns. However, to maintain visual consistency across applications we recommend always starting with the List-Detail pattern. The patterns shown above are a few examples.
Unique 2-deep patterns
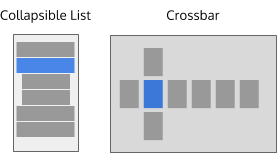
- The Collapsible List pattern is a space-efficient way of showing 2-deep information. The pattern is useful for plasmoids and other applications where the layout must be compact.
- The Crossbar pattern arranges categories vertically and the content within the selected category horizontally. This pattern is often used for navigating video libraries.