Step: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Pipesmoker (talk | contribs) Start up Step page |
Pipesmoker (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Image:Step_rigid_polygons.png|250px|thumb | ]] | |[[Image:Step_rigid_polygons.png|250px|thumb | ]] | ||
|[[Image: | |[[Image:Step_selecting_solver.png|250px|thumb | ]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Image:Step_graphs.png|250px|thumb | ]] | |[[Image:Step_graphs.png|250px|thumb | ]] | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
|[[Image:Step_note.png|250px|thumb | ]] | |[[Image:Step_note.png|250px|thumb | ]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Documentation== | ==Documentation== | ||
Revision as of 16:37, 3 July 2010
Home >> Applications >> Education >> Step

|
Step is an interactive physical simulator. It allows you to explore the physical world through simulations.
It is part of the KDE Education Project. |
Step is an interactive physics simulator. It works like this: you place some bodies on the scene, add some forces such as gravity or springs, then click Simulate and Step shows you how your scene will evolve according to the laws of physics. You can change every property of bodies/forces in your experiment (even during simulation) and see how this will change the outcome of the experiment. With Step you can not only learn but feel how physics works!
Features
- Classical mechanical simulation in two dimensions
- Particles, springs with dumping, gravitational and coulomb forces
- Rigid bodies
- Collision detection (currently only discrete) and handling
- Soft (deformable) bodies simulated as user-editable particles-springs system, sound waves
- Molecular dynamics (currently using Lennard-Jones potential): gas and liquid, condensation and evaporation, calculation of macroscopic quantities and their variances
- Units conversion and expression calculation: you can enter something like "(2 days + 3 hours) * 80 km/h" and it will be accepted as distance value (requires libqalculate)
- Errors calculation and propagation: you can enter values like "1.3 ± 0.2" for any property and errors for all dependent properties will be calculated using statistical formulas
- Solver error estimation: errors introduced by the solver is calculated and added to user-entered errors
- Several different solvers: up to 8th order, explicit and implicit, with or without adaptive timestep (most of the solvers require GSL library)
- Controller tool to easily control properties during simulation (even with custom keyboard shortcuts)
- Tools to visualize results: graph, meter, tracer
- Context information for all objects, integrated wikipedia browser
- Collection of example experiments, more can be downloaded with KNewStuff2
- Integrated tutorials
Screenshots
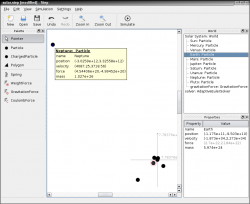 |
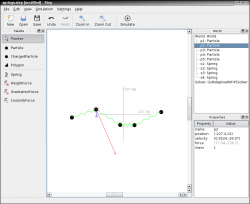 |
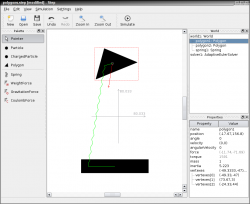 |
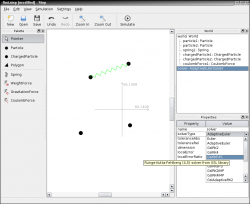 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

