Amarok/Manual/Organization/Collection/RemoteCollections: Difference between revisions
Danielmarth (talk | contribs) |
Danielmarth (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Often it is very comfortable to share your media files across the network. This can be done in different ways. | |||
== | == Ampache == | ||
'''Amarok''' is able to play music from an '''Ampache'''-media-server. '''Ampache''' needs an '''Apache'''-server to work. | |||
=== Server === | |||
= | On '''Debian'''-based distributions like '''Ubuntu''' you can install a '''Ampache'''-server using '''sudo apt-get install ampache'''.<br /> | ||
You need to tell the '''Apache'''-server where it can find the '''Ampache'''-files. Create the file ''/etc/apache2/conf.d/ampache'' with the following content:<br /> | |||
{{Input|1= | |||
Alias /music "/usr/share/ampache/www/" | |||
<directory /> | |||
DirectoryIndex index.php index.html | |||
Options Indexes MultiViews | |||
AllowOverride None | |||
Order allow,deny | |||
Allow from all | |||
</directory> | |||
}} | |||
Restart '''Apache''' with the command ''/etc/init.d/apache2 restart'' so you can access the '''Ampache'''-webinterface using http://localhost/music/ . You get the following page:<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_ampache_installation.png]]<br /> | |||
Choose your language and click <menuchoice>Start configuration</menuchoice> to configure '''Ampache'''. Enter the configuration of your '''MySQL'''-database:<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_ampache_installation1.png]]<br /> | |||
Click <menuchoice>Insert Database</menuchoice> to create the user and database. You will get an error message because there is already a configuration file which is empty. Just enter your '''MySQL'''-configuration again and click <menuchoice>Write Config</menuchoice> and you will get a configuration file as download.<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_ampache_installation3.png]]<br /> | |||
Save this file to ''/usr/share/ampache/www/config/ampache.cfg.php'' and overwrite the existing (empty) configuration. After you clicked <menuchoice>Continue to Step 3</menuchoice> you can create the initial account to manage '''Ampache'''.<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_ampache_installation4]]<br /> | |||
Log into your newly created account:<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_ampache_login.png]]<br /> | |||
And you will get the webinterface:<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_ampache_webinterface.png]]<br /> | |||
Click on <menuchoice>Add a Catalog</menuchoice> in the <menuchoice>Admin</menuchoice> on the left to create a new catalog of music.<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_ampache_catalog.png]]<br /> | |||
Create a new guest account using <menuchoice>Admin -> Add User</menuchoice>:<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_ampache_createuser.png]]<br /> | |||
Now you need to allow guest access on your server. Open the configuration in ''/usr/share/ampache/www/config/ampache.cfg.php'' and remove the ';'-character before ''auto_user = "guest"''. Restart '''Apache''' and the server configuration is finished.<br /> | |||
=== Client === | |||
Activate the '''Ampache''' service using <menuchoice>Settings -> Configure Amarok... -> Internet Services</menuchoice>.<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_ampache_client.png]]<br /> | |||
Configure the service with the data entered on the server:<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_ampache_client1.png]]<br /> | |||
Now the '''Ampache''' service should appear in the left pane.<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_ampache_client2.png]]<br /> | |||
Open the | == Digital Audio Access Protocol (DAAP) == | ||
[[File: | |||
You need to | '''DAAP''' is a protocol to share media in a network. It was first used in the program '''iTunes''', but is widely used today. | ||
=== Server === | |||
On '''Debian'''-based distributions like '''Ubuntu''' you can install a DAAP-server using ''sudo apt-get install mt-daapd''. This will install the '''Firefly'''-DAAP-server. You can configure it using the webinterface by opening the page http://localhost:3689/index.html . The default password is '''mt-daapd''', the user field stays empty.<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_daap_config.png]]<br /> | |||
=== Client === | |||
'''Amarok''' automatically shows the tracks from the server in the left pane and no further configuration is required.<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_daap.png]]<br /> | |||
== Samba == | |||
'''Samba''' is a free implementation of the '''SMB/CIFS''' protocol which is used to share files and printers in a network. Most modern file managers like '''Dolphin''' and '''Nautilus''' support this protocol. | |||
=== Server === | |||
The easiest way is to use your file manager. On '''Debian'''-based distributions like '''Ubuntu''' you can install a '''Dolphin''' extension to manage shares using ''sudo apt-get install kdenetwork-filesharing''. Open the properties of a folder in '''Dolphin''' and switch to the <menuchoice>Share</menuchoice> tab.<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_samba_server.png]]<br /> | |||
After clicking at <menuchoice>Configure File Sharing...</menuchoice> the configuration dialogs is opened.<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_samba_server1.png]]<br /> | |||
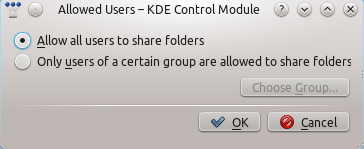
Change the <menuchoice>Allowed Users</menuchoice> to <menuchoice>Allow all users to share folders</menuchoice>.<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_samba_server2.png]]<br /> | |||
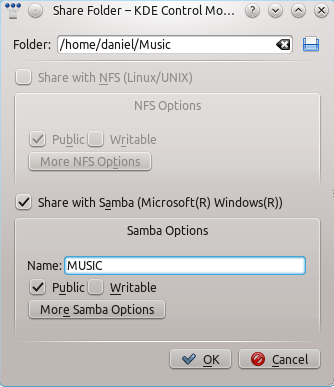
Then you can add the folder to the shares. Click at <menuchoice>Add...</menuchoice> and share the desired folder with '''Samba'''.<br /> | |||
[[File:remotecollections_samba_server3.png]]<br /> | |||
=== Client === | |||
You need to mount the share to use it in '''Amarok'''. To do this, you need to install the package ''smbfs''. Use the command ''sudo mount -t cifs //'''host'''/'''share''' '''/mount-point/''''' to mount the share. After that you can use it like a local folder and add it to your local collection. | |||
== Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) == | |||
'''UPnP''' is a set of protocols to share media on the network. It is also supported by a wide range of Wi-Fi access points. | |||
=== Server === | |||
On '''Debian'''-based distributions like '''Ubuntu''' you can install a '''UPnP'''-server using ''sudo apt-get install ushare''. The service is started in the terminal with the command '' ushare -n '''servername''' [-i '''interface'''] [-c '''folder''']''. You can also manage shares using the webinterface, which you can access by opening http://127.0.0.1:port/web/ushare.html in the browser. ''port'' needs to be adjusted to your settings. | |||
=== Client === | |||
You also need a '''UPnP'''-client, which can be installed using ''sudo apt-get install djmount''. '''UPnP''' discovery can be started using ''djmount '''mountpoint'''''. After that you can use it like a local folder and add it to your local collection. | |||
Revision as of 23:27, 17 December 2010
Introduction
Often it is very comfortable to share your media files across the network. This can be done in different ways.
Ampache
Amarok is able to play music from an Ampache-media-server. Ampache needs an Apache-server to work.
Server
On Debian-based distributions like Ubuntu you can install a Ampache-server using sudo apt-get install ampache.
You need to tell the Apache-server where it can find the Ampache-files. Create the file /etc/apache2/conf.d/ampache with the following content:
Alias /music "/usr/share/ampache/www/"
<directory />
DirectoryIndex index.php index.html
Options Indexes MultiViews
AllowOverride None
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
</directory>
Restart Apache with the command /etc/init.d/apache2 restart so you can access the Ampache-webinterface using http://localhost/music/ . You get the following page:

Choose your language and click to configure Ampache. Enter the configuration of your MySQL-database:
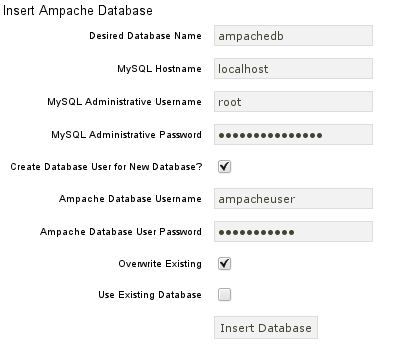
Click to create the user and database. You will get an error message because there is already a configuration file which is empty. Just enter your MySQL-configuration again and click and you will get a configuration file as download.
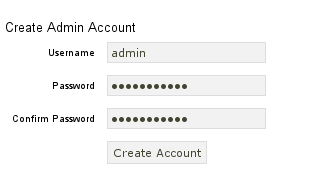
Save this file to /usr/share/ampache/www/config/ampache.cfg.php and overwrite the existing (empty) configuration. After you clicked you can create the initial account to manage Ampache.
File:Remotecollections ampache installation4
Log into your newly created account:
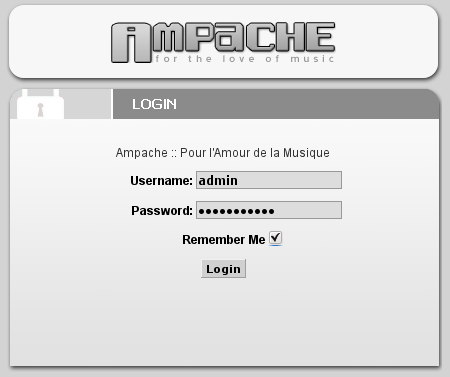
And you will get the webinterface:
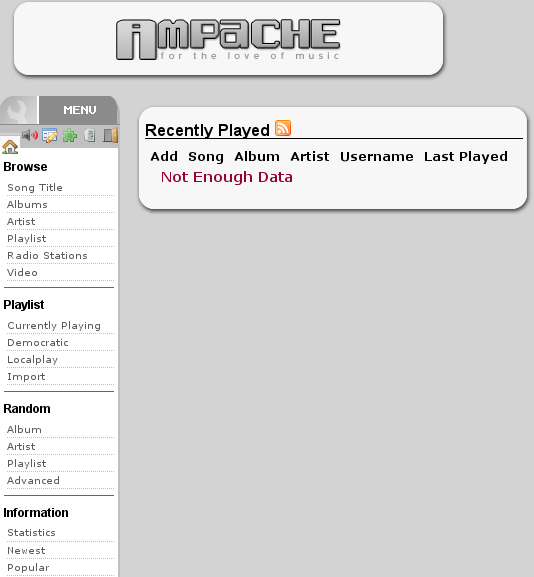
Click on in the on the left to create a new catalog of music.
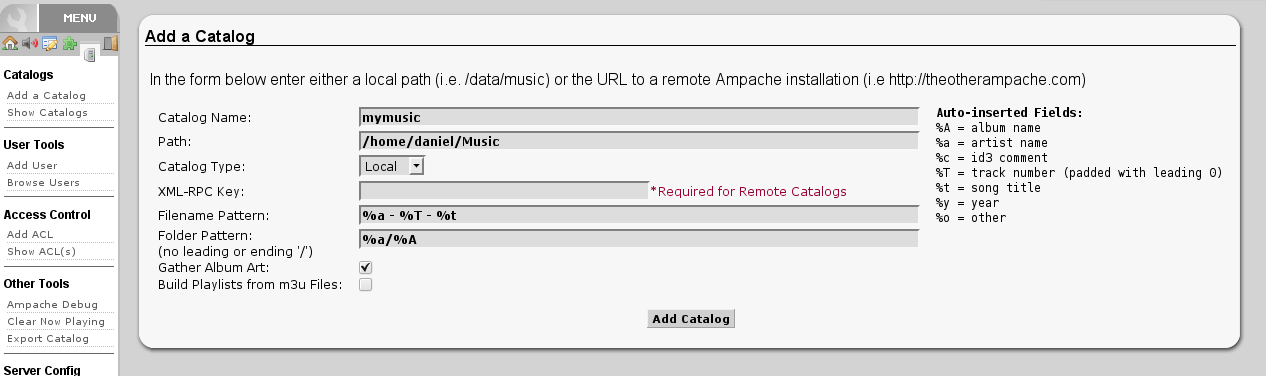
Create a new guest account using :
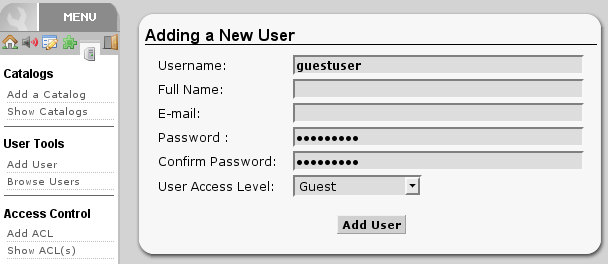
Now you need to allow guest access on your server. Open the configuration in /usr/share/ampache/www/config/ampache.cfg.php and remove the ';'-character before auto_user = "guest". Restart Apache and the server configuration is finished.
Client
Activate the Ampache service using .
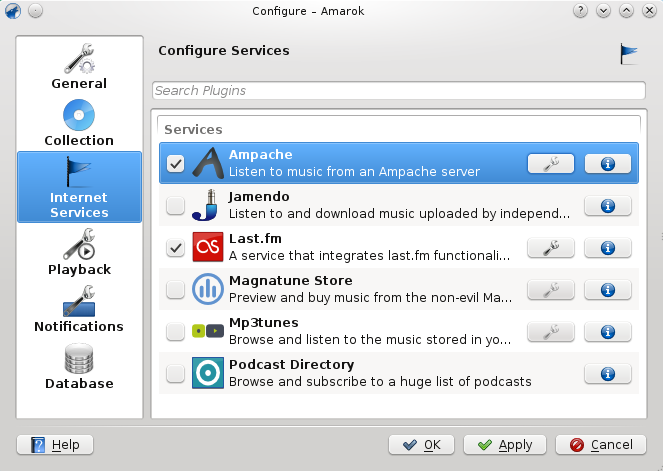
Configure the service with the data entered on the server:
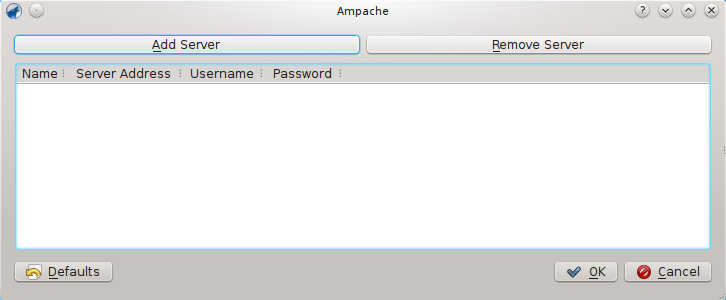
Now the Ampache service should appear in the left pane.

Digital Audio Access Protocol (DAAP)
DAAP is a protocol to share media in a network. It was first used in the program iTunes, but is widely used today.
Server
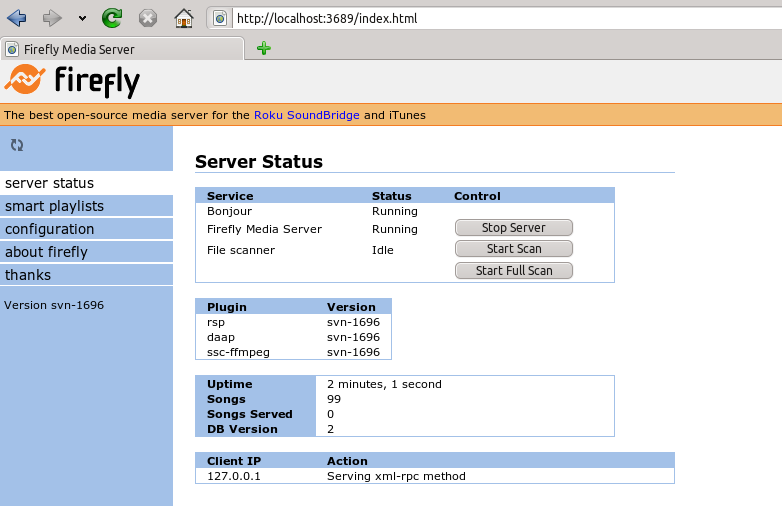
On Debian-based distributions like Ubuntu you can install a DAAP-server using sudo apt-get install mt-daapd. This will install the Firefly-DAAP-server. You can configure it using the webinterface by opening the page http://localhost:3689/index.html . The default password is mt-daapd, the user field stays empty.
Client
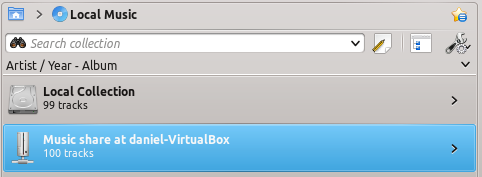
Amarok automatically shows the tracks from the server in the left pane and no further configuration is required.
Samba
Samba is a free implementation of the SMB/CIFS protocol which is used to share files and printers in a network. Most modern file managers like Dolphin and Nautilus support this protocol.
Server
The easiest way is to use your file manager. On Debian-based distributions like Ubuntu you can install a Dolphin extension to manage shares using sudo apt-get install kdenetwork-filesharing. Open the properties of a folder in Dolphin and switch to the tab.
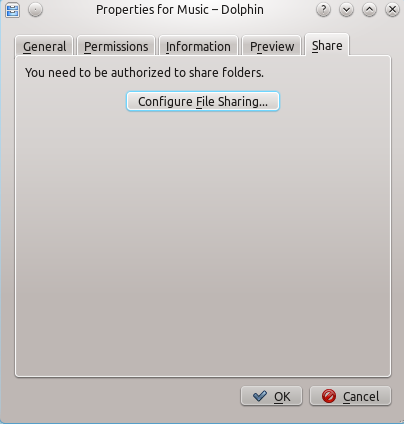
After clicking at the configuration dialogs is opened.
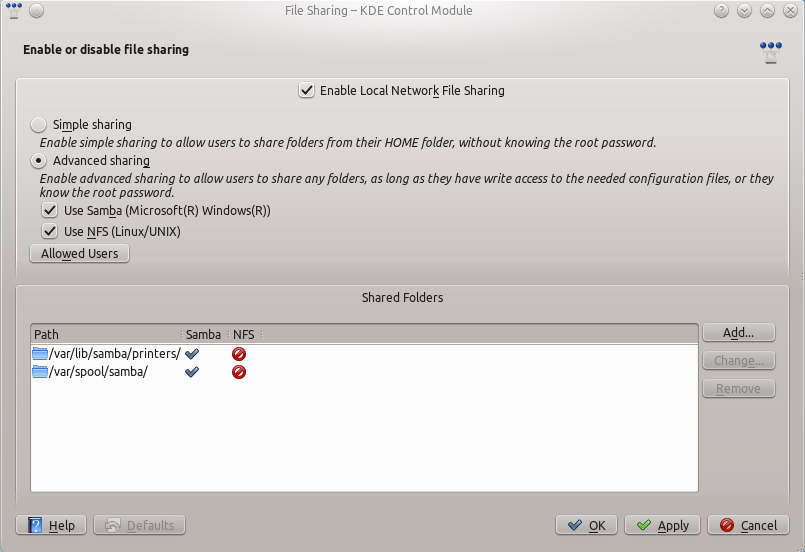
Change the to .
Then you can add the folder to the shares. Click at and share the desired folder with Samba.
Client
You need to mount the share to use it in Amarok. To do this, you need to install the package smbfs. Use the command sudo mount -t cifs //host/share /mount-point/ to mount the share. After that you can use it like a local folder and add it to your local collection.
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP)
UPnP is a set of protocols to share media on the network. It is also supported by a wide range of Wi-Fi access points.
Server
On Debian-based distributions like Ubuntu you can install a UPnP-server using sudo apt-get install ushare. The service is started in the terminal with the command ushare -n servername [-i interface] [-c folder]. You can also manage shares using the webinterface, which you can access by opening http://127.0.0.1:port/web/ushare.html in the browser. port needs to be adjusted to your settings.
Client
You also need a UPnP-client, which can be installed using sudo apt-get install djmount. UPnP discovery can be started using djmount mountpoint. After that you can use it like a local folder and add it to your local collection.
