KDevelop4/Manual/Building (compiling) projects with custom Makefiles/uk: Difference between revisions
Created page with "=== Вибір збірки цілей з Makefile для регулярного збирання ===" |
Created page with "=== Обробка повідомлень про помилки ===" |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
jobs "make" should execute — if your computer has, say, 8 processor cores, then entering 8 in this field would be a useful choice. In this dialog, the <menuchoice>Default make target</menuchoice> is a Makefile target used for '''all''' targets in the selection. | jobs "make" should execute — if your computer has, say, 8 processor cores, then entering 8 in this field would be a useful choice. In this dialog, the <menuchoice>Default make target</menuchoice> is a Makefile target used for '''all''' targets in the selection. | ||
<span id="What to do with error messages"></span> | <span id="What to do with error messages"></span> | ||
=== | === Обробка повідомлень про помилки === | ||
If the compiler encounters an error message, simply click on the line with the error message and the editor will jump to the line (and if available column) where the error was reported. Depending on the error message, '''KDevelop''' may also offer you several possible actions to fix the error, for example by declaring a previously undeclared variable if an unknown symbol was found. | If the compiler encounters an error message, simply click on the line with the error message and the editor will jump to the line (and if available column) where the error was reported. Depending on the error message, '''KDevelop''' may also offer you several possible actions to fix the error, for example by declaring a previously undeclared variable if an unknown symbol was found. | ||
Revision as of 08:52, 20 May 2011
Збирання (компіляція) проектів з нетиповими Makefile
Many projects describe how source files have to be compiled (and which files have to be recompiled once a source or header file changes) using Makefiles that are interpreted by the make program (see, for example, GNU make). For simple projects, it is often very easy to set up such a file by hand. Larger projects often integrate their Makefiles with the GNU autotools (autoconf, autoheader, automake). In this section, let us simply assume that you have a Makefile for your project and you want to teach KDevelop how to interact with it.
The first step is to teach KDevelop about targets in your Makefiles. There are two ways to do that: selecting individual Makefile targets, and choosing a set of targets you may want to build frequently. For both approaches, open
the tool by clicking on the button on the perimeter of KDevelop's main window (if you don't have this button see above how to add a tool's button there). The tool window has two parts: the top half — titled — lists all of your projects and let's you expand the underlying directory trees. The bottom half — titled — lists a subset of those projects that will be built if you choose the menu item or hit F8; we'll come back to this part below.
Збирання окремих цілей з Makefile
In the top part of the project view, expand the sub-tree for one project, let's say the one for which you want to run a particular Makefile target. This will give you icons for (i) directories under this project, (ii) files in the top-level directory for this project, (iii) Makefile targets KDevelop can identify. These categories are shown in the picture at right. Note that KDevelop understands Makefile syntax to a certain degree and therefore can offer you targets defined in this Makefile (though this understanding has its limits if targets are composed or implicit).
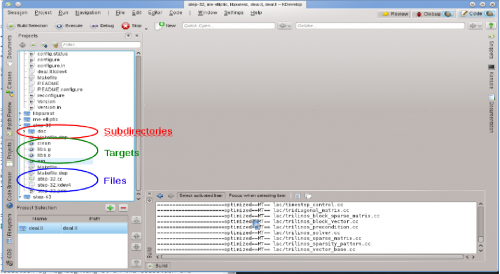
To build any of the targets listed there, click on it with the right mouse button and select . For example, doing this with the "clean" target will simply execute "make clean". You can see this happening in the subwindow titled that opens up, showing the command and the output. (This window corresponds to the tool, so you can close and later re-open the window using the tool button on the perimeter of the main window. It is shown at the bottom right of the picture.)
Вибір збірки цілей з Makefile для регулярного збирання
Right-clicking on individual Makefile targets every time you want to build something will quickly get old. Rather, we'd like to have individual targets for one or more of the projects in the session that we can repeatedly build without much mouse work. This is where the concept of "Build target selections" comes in: it is a collection of Makefile targets that are built one-after-the-other whenever you hit the button in the button list at the top, select the menu item, or hit the F8 function key.
The list of selected Makefile targets is shown in the bottom half of the tool view. By default, the selection contains all projects, but you can change that. For example, if your list of projects contains three projects (a base library L and two applications A and B), but you're currently only working on project A, then you may want to remove project B from the selection by highlighting it in the selection and hitting the red button. Furthermore, you probably want to make sure that the library L is built before project A by moving entries in the selection up and down using the buttons to the right of the list. You can also get a particular Makefile target into the selection by right-clicking onto it and selecting , or just highlighting it and hitting the green button just above the list of selected targets.
KDevelop allows you to configure what to do whenever you build the selection. To this end, use the menu item . There, you can for example select the number of simultaneous jobs "make" should execute — if your computer has, say, 8 processor cores, then entering 8 in this field would be a useful choice. In this dialog, the is a Makefile target used for all targets in the selection.
Обробка повідомлень про помилки
If the compiler encounters an error message, simply click on the line with the error message and the editor will jump to the line (and if available column) where the error was reported. Depending on the error message, KDevelop may also offer you several possible actions to fix the error, for example by declaring a previously undeclared variable if an unknown symbol was found.

