Archive:Kdenlive/Manual/Effects/Alpha manipulation/Color Selection/en: Difference between revisions
Updating to match new version of source page |
Importing a new version from external source |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==== Color Selection ==== | ==== Color Selection ==== | ||
The '''Colour Selection''' effect (or '''Color Selection''') is a more advanced version of the [https://userbase.kde.org/Kdenlive/Manual/Effects/Alpha_manipulation/Blue_Screen Chroma Key] effect. Colour Selection allows for some basic feathering (by changing the '''Edge Mode''') and much more fine-grained control over how much & in which way you remove the background. | |||
This is | This is better for backgrounds that have less contrast with the foreground, or more complex backgrounds. For simple backgrounds (such as green, blue, red or possibly black), use the [https://userbase.kde.org/Kdenlive/Manual/Effects/Alpha_manipulation/Blue_Screen Chroma Key] effect. | ||
===Basic Technique=== | |||
This section currently has no text. I will complete it later, right now I do not have the time. | |||
=== All Options=== | |||
[[File:Color_selection_effect.png]] | [[File:Color_selection_effect.png]] | ||
'''Color to select''': the color to select. This is the | Here is a outline of all the options: | ||
'''Color to select''': the color to select. This is the color that will be transparent/the only colour that is opaque. | |||
'''Invert selection''': When ON, the selected color will be transparent | '''Invert selection''': When ON (default), the selected color will be transparent. When OFF the selected color will be opaque. Keeping the selected colour opaque may be more effective if the foreground is simple and the background is complicated | ||
'''Selection Subspace''' options are: RGB (Red Green Blue), ABI and HCI (Hue Chromacity Intensity) | '''Selection Subspace''' options are: RGB (Red Green Blue), ABI and HCI (Hue Chromacity Intensity) | ||
These different options yield different results. While RGB should yield the sharpest and best results, sometimes (as [https://userbase.kde.org/User:TheMickyRosen-Left I] have seen from experience) the other option, HCI & ABI, can yield much better results then RGB. So if RGB isn't producing good results then try on of the other options. Note:'''Previews of video chroma keyed using HCI will be slow''' since it has to calculate values for every single pixel. | |||
Here is the same thing specified in confusing computerspeak: | |||
Specifies in which of the three color spaces (RGB, ABI, HCI) the delta controls will work. Both ABI and HCI are separated luma/chroma. HCI is a cylindrical "Hue Chromacity Intensity" space, and ABI is a cartesian version thereof. Both suffer from chroma subsampling, and will give less sharp results than RGB. Note:HCI is slow, because it has to calculate atan2() and hypot() for each pixel. | |||
'''Subspace Shape''' options are: Box, Ellipsoid, Diamond | '''Subspace Shape''' options are: Box, Ellipsoid, Diamond | ||
| Line 31: | Line 35: | ||
'''Edge Mode''' Options are: Hard, Fat, Normal, Skinny, Slope | '''Edge Mode''' Options are: Hard, Fat, Normal, Skinny, Slope | ||
"Hard" | "Hard" there is no feathuring. Any part of the image/video is either fully opaque and fully transparent. This means there will be no blue between the removed parts and the remaining parts whatsoever, and this option is useful if your chroma key turned out to be perfect. | ||
The remaining options ("Fat", "Normal" and "Skinny") create a gradual transition between transparent and opaque | The remaining options ("Fat", "Normal" and "Skinny") create a gradual transition between transparent and opaque. The fatter the choice, the more the selected areas are filled towards the rim (AKA more feathuring for fatter choices). This is useful if your colour selection did not turn out that well. | ||
'''Operation''' options are: Write On Clear, Max, Min, Add and Subtract. This defines how to deal with an existing alpha channel in the clip. See [[Kdenlive/Manual/Effects/Alpha_manipulation/Alpha_shapes#Operations|Alpha Shapes]] for the meanings of these operations. | '''Operation''' options are: Write On Clear, Max, Min, Add and Subtract. This defines how to deal with an existing alpha channel in the clip. See [[Kdenlive/Manual/Effects/Alpha_manipulation/Alpha_shapes#Operations|Alpha Shapes]] for the meanings of these operations. | ||
Revision as of 05:00, 1 October 2018
Color Selection
The Colour Selection effect (or Color Selection) is a more advanced version of the Chroma Key effect. Colour Selection allows for some basic feathering (by changing the Edge Mode) and much more fine-grained control over how much & in which way you remove the background.
This is better for backgrounds that have less contrast with the foreground, or more complex backgrounds. For simple backgrounds (such as green, blue, red or possibly black), use the Chroma Key effect.
Basic Technique
This section currently has no text. I will complete it later, right now I do not have the time.
All Options
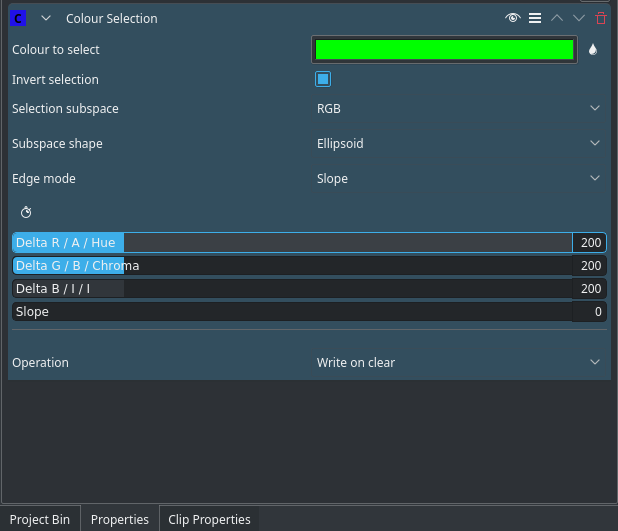
Here is a outline of all the options:
Color to select: the color to select. This is the color that will be transparent/the only colour that is opaque.
Invert selection: When ON (default), the selected color will be transparent. When OFF the selected color will be opaque. Keeping the selected colour opaque may be more effective if the foreground is simple and the background is complicated
Selection Subspace options are: RGB (Red Green Blue), ABI and HCI (Hue Chromacity Intensity)
These different options yield different results. While RGB should yield the sharpest and best results, sometimes (as I have seen from experience) the other option, HCI & ABI, can yield much better results then RGB. So if RGB isn't producing good results then try on of the other options. Note:Previews of video chroma keyed using HCI will be slow since it has to calculate values for every single pixel.
Here is the same thing specified in confusing computerspeak:
Specifies in which of the three color spaces (RGB, ABI, HCI) the delta controls will work. Both ABI and HCI are separated luma/chroma. HCI is a cylindrical "Hue Chromacity Intensity" space, and ABI is a cartesian version thereof. Both suffer from chroma subsampling, and will give less sharp results than RGB. Note:HCI is slow, because it has to calculate atan2() and hypot() for each pixel.
Subspace Shape options are: Box, Ellipsoid, Diamond
Determines the shape of the color subspace. Options are: box, ellipsoid or diamond. Box is the biggest of them (by volume) and diamond the smallest. Imagine an octahedron inscribed inside an ellipsoid, which is in turn inscribed in a box. The tips of the diamond touch the ellipsoid, and the box, at the center of the sides of the box.
Edge Mode Options are: Hard, Fat, Normal, Skinny, Slope
"Hard" there is no feathuring. Any part of the image/video is either fully opaque and fully transparent. This means there will be no blue between the removed parts and the remaining parts whatsoever, and this option is useful if your chroma key turned out to be perfect.
The remaining options ("Fat", "Normal" and "Skinny") create a gradual transition between transparent and opaque. The fatter the choice, the more the selected areas are filled towards the rim (AKA more feathuring for fatter choices). This is useful if your colour selection did not turn out that well.
Operation options are: Write On Clear, Max, Min, Add and Subtract. This defines how to deal with an existing alpha channel in the clip. See Alpha Shapes for the meanings of these operations.
The "min", "max", "add" and "subtract" options allow cascading of select0r plugins (or combination with other alpha-writting plugins). These options combine the current selection with the pre-existing alpha of the source material. This way complex selections can be built.
Delta XXXX: These three parameters determine the size of the color subspace along each axis. Bigger value means bigger tolerance on that axis.
For example, setting a high I delta (in ABI and HCI), will allow the selection of a specific color in both light and shadows, but will also discard most of the high-bandwidth luma signal, making the selection less spatially accurate.
Slope: When "Edge mode" is set to "Slope", this parameter sets the gradualness of the transition between opaque and transparent
See Also
See also Blue Screen which does color based alpha selection but is a bit simpler.
This page covers some Color Theory to help understand Hue, Chroma, Luminance etc.