KWin Rules
Overview
KWin allows the end-user to define rules to alter the behavior of an application's windows.
For example, when an application is started, it can be forced to always run on Virtual Desktop #2. Or a defect in an application can be worked-around by using a rule to, say, always force the window on top of all others.
This page will define the different settings and the attributes. For the impatient folks, working examples will be listed. Whenever possible, screen shots will be used to show example settings.
Examples
The environment in these examples has eight Virtual Desktops.
The first example details all the steps. Subsequent examples only list steps specific to the example.
Pin a Window to a Desktop and with a favorite Size and Position
Pin Akregator to Virtual Desktop 2. Additionally, start the application with a preferred size and position.
The KWin rule is created as follows:
- Start Akregator on desktop two, size and place it to suit:
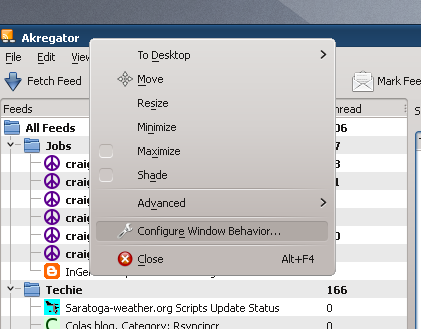
- Right-click on the menu bar and select Configure Window Behavior...:
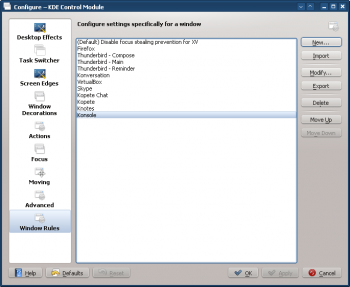
- Select the Window Rules option in the left column and click on the New... button:
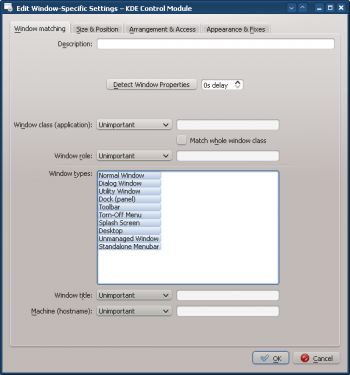
- The Edit Window-Specific Settings window is displayed. The Window matching tab is the default tab:
- Click on Detect Window Properties and with 0s delay the cursor immediately turns into cross-hairs. Click (anywhere) inside the Akregator window (but not the title bar). The window criteria are presented. Match only by primary class name so leave the check boxes unchecked:
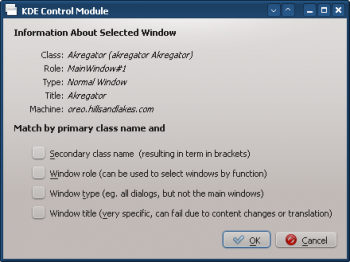
- Clicking OK in the previous window back-fills the results in the Window Matching tab. Enter a meaningful Description (which is displayed in the KWin Rule window):
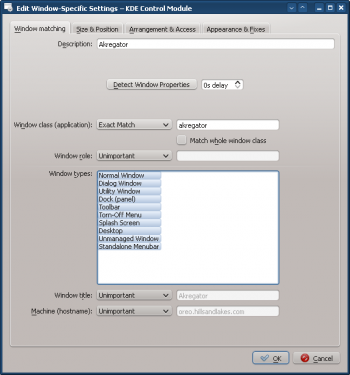
- Enable the window attributes: Position, Size and Desktop. The values are automatically set by Detect Window Properties:
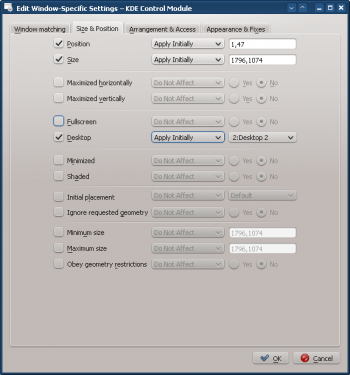
- Clicking OK in the previous window returns to the main KWin Rules. The new rule with its Description is listed:
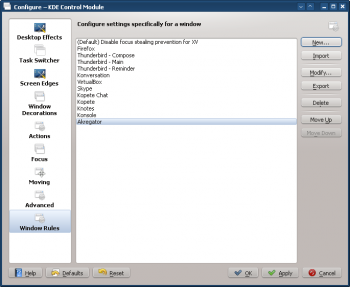
- Click OK to close the window.
- Done.
Display Application on all Desktops and treat certain Children Windows Differently
Except for conversation windows, display Kopete and its children windows on all desktops and skip the systray and pager (the Virtual Desktop view in systray). For conversation windows, treat them as the parent window except show them in systray.
In order to implement the above, two rules need to be created:
- A rule for Kopete Chat and
- A rule for Kopete
The Kopete Chat rule's matching-criteria is more restrictive than the Kopete rule as it needs to match a specific Window Role: the chat window. Due to rule evaluation (pablo - make this a link to the respective section), the Kopete Chat rule must precede Kopete rule in the KWin Rule list.
Kopete Chat Rule
Assuming a Kopete Chat window is open:
- Use Detect Window Properties and select the Kopete Chat window. Check the Window role box to restrict the criteria to chat windows:
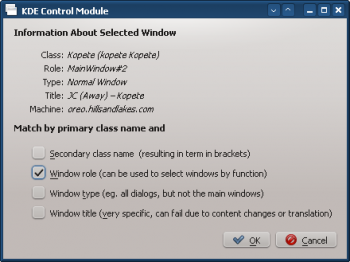
- Clicking OK in the previous window back-fills the results in the Window Matching tab. Enter a meaningful Description:
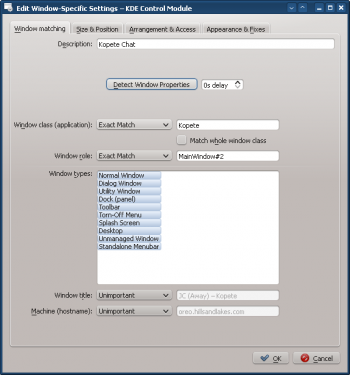
- Enable the following attributes:
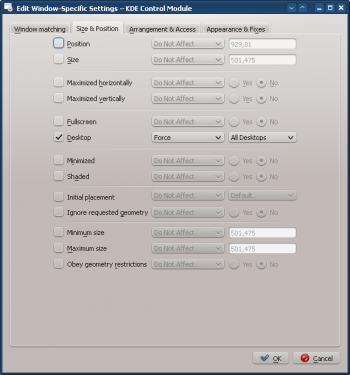
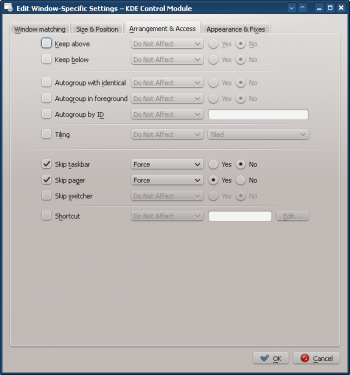
- Click through to complete entry of the rule.
Kopete Rule
Assuming Kopete is open:
- Use Detect Window Properties and select the Kopete window. Check the Secondary class name box to include all of Kopetes children windows:
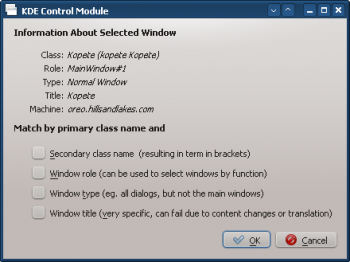
- Clicking OK in the previous window back-fills the results in the Window Matching tab. Enter a meaningful Description:
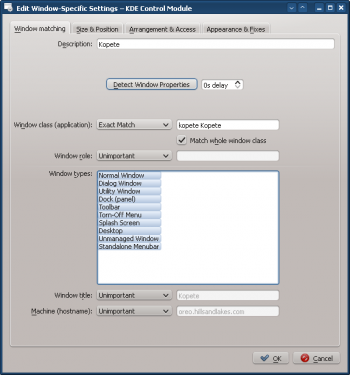
- Enable the following attributes:
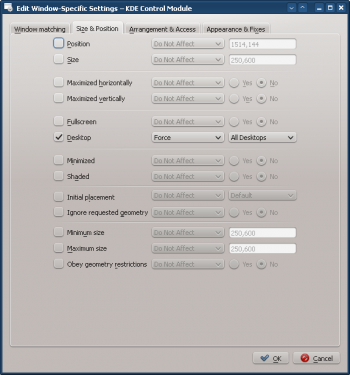
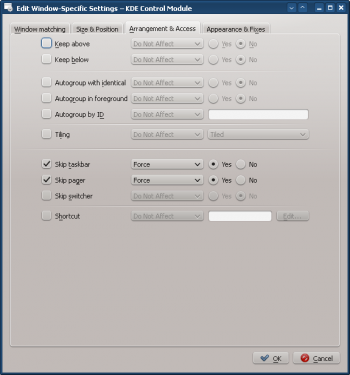
- Click through to complete entry of the rule.
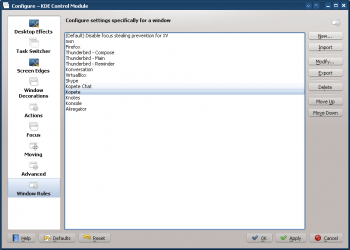
KWin Rule List
As mentioned above, the Kopete Chat rule must precede the Kopete rule:
Suppress a Window showing on Pager
Good for knotes
Force a Window to the Top
Multiple Rules per Application
e.g. Thunderbird on one desktop and composition window on any
Pop Active Window to the Front/Top
KWin Rule Editor
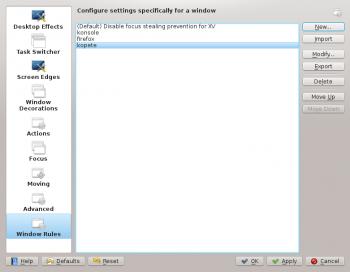
Invoking the Editor
There are several ways one can invoke the Rules editor. Below are a couple:
- Right-click on the title-bar of any window, choose and in the Configure window, select or
Anatomy
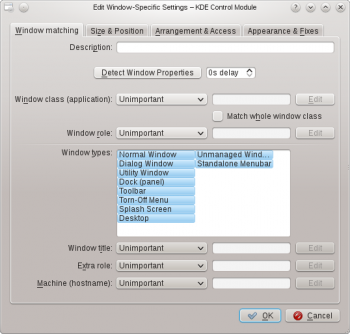
The editor is composed of four tabs:
As the name implies, is used to specify criteria to match one or more windows. The other three tabs are used to alter the characteristics of the matching windows.
Rule Evaluation
When an application starts (or the rules are modified), KWin evaluates the rules from the top of the list until either a matching rule is found or the list is exhausted. If a rule matches, the attributes set in the rule are applied to the window and the window is displayed.
Window Matching
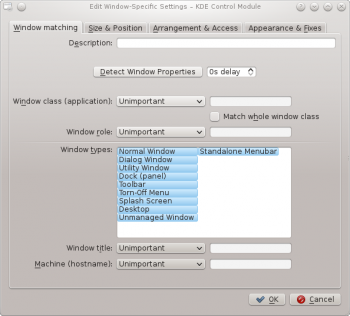
The tab provides a series of matching-criteria fields used to identify application windows:
- - match this window and all its children windows.
- and
- - restrict the match to the function of the window (e.g. a main window, a chat window, etc.)
- - restrict the match to the type of window: Normal Window, Dialog Window, etc.
- - restrict the match to the title of the window.
- - restrict the match to the host name associated with the window.
For each field, the following operators can be applied against the field value:
- - case insensitive.
- - Qt's regular expressions are implemented. For additional information, web search qt regex nokia.
Detect Window Properties
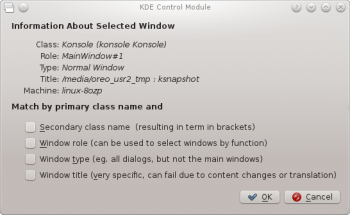
The function simplifies the process of entering the matching-criteria.
- For the application you'd like to create a rule, start the application.
- Next, in the tab, set the number of seconds of delay before the function starts. The default is zero seconds.
- Click on and
- When the mouse-cursor turns to cross-hairs, place it inside the application window and left-click.
- A new window is presented with information about the selected window:
- Class
- Role
- Type
- Title
- Machine (hostname)
Click the button to back-fill the criteria.
By using a combination of the information, you can tailor whether a rule applies to an entire application (by Class) or a to a specific window Type within the Class - say a Toolbar.
Window Attributes
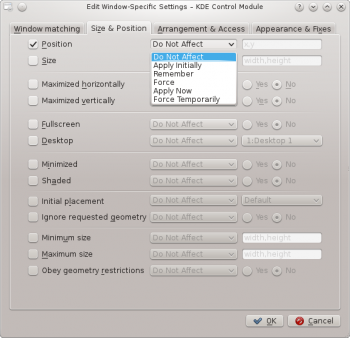
The attributes which can be set are grouped in three tabs:
Each attribute has additional settings which determine when they're applied and depending on the attribute, there may be an additional argument.
Parameters
Each attribute minimally accepts one of the following parameters. Additional, attribute-specific arguments are listed within each attribute definition.
- Do Not Affect
- Unset the attribute.
- Apply Initially
- Start the window with the attribute and allow it to be changed at run-time.
- Remember
- Use the attribute setting as defined in the rule and if changed at run-time, save and use the new value instead.
- Force
- The setting cannot be changed at run-time.
- Apply Now, Force Temporarily
- Apply/Force the setting once and unset the attribute.
Apply Now allows the attribute to be changed at run-time. Use Force Temporarily to not allow the attribute to be changed.
Attributes
Size & Position
- Position
- Position the window's upper left corner at the specified x,y coordinate.
- Size
- The width and height of the window.
- Maximized horizontally, Maximized vertically, Fullscreen
- These attributes are used to toggle the maximum horizontal/minimum horizontal/full-screen window attribute.
- Desktop
- Place the window on the specified (Virtual) Desktop. Use All Desktops to place the window on all Virtual Desktops.
- Minimized, Shaded
- Toggle the Minimize and Shading window attribute. For example, a window can be started Minimized or if it is started Minimized, it can be forced to not.
- Initial placement
- Override the global window placement strategy with one of the following:
- Default - use the global window placement strategy.
- No Placement - top-left corner.
- Smart - place where no other window exists.
- Maximizing - start the window maximized.
- Cascade
- Centered
- Random
- Top-Left Corner
- Under Mouse
- On Main Window - restrict placement of a child window to the boundaries of the parent window.
- Ignore requested geometry
- Toggle whether to accept or ignore the window's requested geometry and ignore the global placement strategy.
- Minimum size, Maximum size
- The minimum and maximum size allowed for the window.
- Obey geometry restrictions
- Toggle whether to adhere to the window's requested aspect ratio.
Arrangement & Access
- Keep above, Keep below
- Toggle whether to keep the window above/below all others.
- Autogroup with identical
- Toggle the grouping (commonly known as tabbing) of windows.
- Autogroup in foreground
- Toggle whether to make the window active when it is added to the group.
- Autogroup by ID
- Create a group via a user-defined ID. More than one rule can share the same ID to allow for seemingly unrelated windows to be grouped.
- Tiling
- Override the default window behavior to either Tiled or Floating.
- Skip taskbar
- Toggle whether to display the window in the taskbar.
- Skip pager
- Toggle whether to display the window in the virtual desktop list.
- Skip switcher
- Toggle whether to display the window in the ALT+TAB list.
- Shortcut
- Assign a shortcut to the window. When Edit... is clicked, additional instructions are presented.
Appearance & Fixes
- No titlebar and frame
- Toggle whether to display the titlebar and frame.
- Active/Inactive opacity
- When the window is active/inactive, set its opacity to the percentage specified.
- Moving/resizing
- Deprecated as of >4.8
- Focus stealing prevention
- When a window wants focus, control on a scale (from None to Extreme) whether to honor the focus request and place the window on top above all other windows and give it focus, or ignore its request (potentially leaving the window behind other windows).
- None - Always grant focus to the window.
- Low
- Normal
- High
- Extreme - The window's focus request is denied. Focus is only granted by mousing to the window.
- Accept focus
- Toggle whether the window accepts keyboard input. Make the window read-only.
- Ignore global shortcuts
- Toggle whether to ignore global shortcuts while the window is active.
- Closeable
- Toggle whether to display the Close button on the title bar.
- Window type
- Change the window to another type and inherit the characteristics of that window:
- Normal Window
- Dialog Window
- Utility Window
- Dock (panel)
- Toolbar
- Torn-Off Menu
- Splash Screen
- Desktop
- Standalone Menubar
- Block compositing
- Toggle whether to disable compositing while the window exists. If compositing is enabled and the rule specifies to disable compositing, once the window exists, compositing will be re-activated.



