Amarok/Manual/Organization/Collection/RemoteCollections/Samba: Difference between revisions
Bypassed redirection page |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
{{Prevnext2 | {{Prevnext2 | ||
| prevpage=Amarok/Manual/ | | prevpage=Amarok/Manual/Collection/RemoteCollections/DAAP | nextpage=Amarok/Manual/Collection/RemoteCollections/UPnP | ||
| prevtext=DAAP | nexttext=UPnP | | prevtext=DAAP | nexttext=UPnP | ||
| index= Amarok/Manual | indextext=Back to Menu | | index= Amarok/Manual | indextext=Back to Menu | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 14:03, 11 June 2011
Samba
Samba is a free implementation of the SMB/CIFS protocol which is used to share files and printers in a network. Most modern file managers like Dolphin and Nautilus support this protocol.
Client
You need to mount the share to use it in Amarok. To do this, you need to install the package smbfs. Use the command
sudo mount -t cifs //'''host'''/'''share''' '''/mount-point/'''
to mount the share. After that you can use it like a local folder and add it to your local collection.
Server
The easiest way is to use your file manager. On Debian-based distributions like Ubuntu you can install a Dolphin extension to manage shares using
sudo apt-get install kdenetwork-filesharing
Open the properties of a folder in Dolphin and switch to the tab.
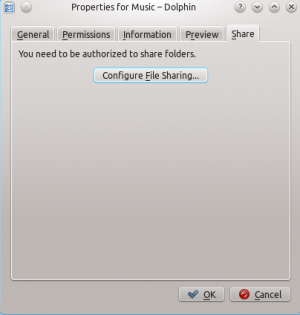
Click to open the configuration dialog.
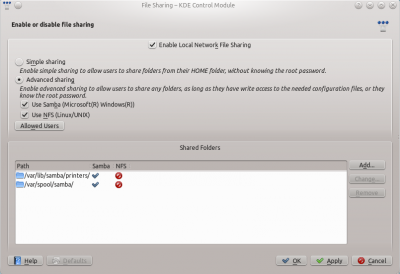
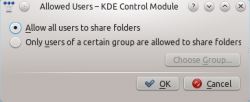
Change the settings to and the to .
Then you can add the folder to the shares. Click at and share the desired folder with Samba.
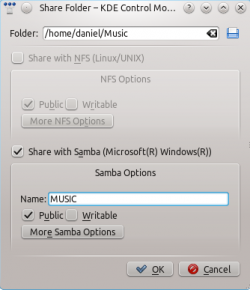
The folder should now be accessible to the network.
