Kexi/Tutorials/Drilling Down on Facebook Data/da: Difference between revisions
Importing a new version from external source |
Importing a new version from external source |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
Felterne har et navn, en type og en kommentar og også adskillige egenskaber, som er tilgængelige i egenskabseditoren i højre side, så som begrænsninger og en standardværdi, hvis ingen værdi angives. Hvert objekt i databasen vil have mange egenskaber tilknyttet, og egenskabseditoren lader dig se og redigere dem et sted. | Felterne har et navn, en type og en kommentar og også adskillige egenskaber, som er tilgængelige i egenskabseditoren i højre side, så som begrænsninger og en standardværdi, hvis ingen værdi angives. Hvert objekt i databasen vil have mange egenskaber tilknyttet, og egenskabseditoren lader dig se og redigere dem et sted. | ||
Skifter man til datavisning, så spørges der om tabellen skal gemmes og tabeldataeditoren vises, så man manuelt kan indskrive poster, med deet er ikke særlig sjovt! | |||
== Getting The Data == | == Getting The Data == | ||
Revision as of 08:14, 8 September 2012
Introduktion
Dene artikel tager en ny bruger igennem en række begreber i Kexi, Koffices program til håndtering af databaser. Kexis funktioner går fra simpel oprettelse af tabeller og forespørgsler til mere avanceret rapportering og scriptning. Kexi er netop blevet udgivet som en del af KOffice 2.2. Denne artikel er rettet mod nye brugere og eksisterende brugere af Kexi 1.6 som en demonstration af, hvor brugbar Kexi kan være.
Kexi 2 har været 3 år i udvikling for at komme fra Kexi 1.6 til den nuværende tilstand og nåede ikke at komme med i udgivelserne af KOffice 2.0 og 2.1 på grund af det lille antal udviklere. Helt i open-source-ånden arbejder Kexis udviklere i deres fritid som en hobby. Det håbes, at denne første udgave nu er stabil nok til at blive brugt og vil være noget, det kan bygges videre på i fremtidige udgivelser.
Når man skal skrive en brugbar vejledning er det nyttigt at have et virkeligt eksempel at arbejde med. Som ejer af Kexis Facebook-side[1] får jeg hver uge opdateringer via e-mail med diverse statistikker. Målet med denne artikel er at få disse data ud af e-mailene og ind i en Kexi-database for at blive i stand til at udføre søgninger i dem og lave rapporter over dem for at vise tendenser over tid.
De rå data
For at få data til databasen eksporterede jeg et udvalg af data fra KMail. Dette oprettede en .mbox-fil, som i bund og grund er en tekstfil, som indeholder alle e-mailene. Det ville hvae været muligt at gå igennem hver mail og skrive detaljerne ind i en tabel, men da jeg allerede har nogle mails liggende, så ønskede jeg indsamle data automatisk, og det er en god udfordring til at skrive et script i Kexi til at gøre dette.
Første skridt, lav en database og tabel
Hvis Kexi ikke er inkluderet i din installation, så se om den er tilgængelig som en opdatering i din pakkehåndtering. Hvis ikke, så skal du installere den fra kilden ved at følge vejledningerne på KOffices[2] websted og KDE's wikier[3].
Jeg begynder med at starte Kexi op og vælger at lave en fra guiden Nyt projekt. Afhængigt af, hvilke plugins du har installeret vil du kunne oprette en database gemt som en fil eller på en eksisterende databaseserver som PostgreSQL eller MySQL. Det nemmeste for en ny bruger er at vælge at gemme i en fil, og det er også passende, når der kun vil være et begrænset antal bruger af databasen i gang samtidigt. Kexis filbaserede databaser bruger sqlite som det underliggende format og kan derfor læses af ethvert sqlite-kompatibelt program.
Databasen skal have et navn; jeg valgte kexi_facebook fulgt at en placering, hvor den skal gemmes – standarden er ok. Jeg blev så præsenteret for Kexis hovedvindue. Hovedvinduet indeholder en værktøjslinje langs toppen og en projektnavigator ned langs venstre side. Hovedværktøjslinjen i Kexi er forskellig fra de andre KOffice-programmer og bruger et layout med faneblade. Hvert vindue der åbnes har også sin egen lokale værktøjslinje til funktioner, som er specifikke for det vindue, så som tabeller, forespørgsler, formularer, rapporter og scripts.
I fanebladet i den øverste menu valgte jeg for at starte tabeldesigneren.
Statistikken jeg modtager via e-mail inkluderer dato, antal nye fans, antal wall posts, antal besøg og det samlede antal fans, så jeg lavede en tabel med følgende designskema:
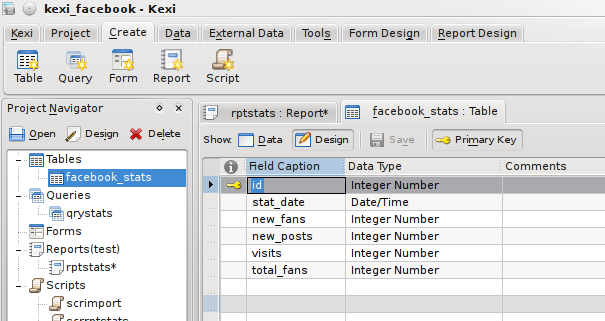
Felterne har et navn, en type og en kommentar og også adskillige egenskaber, som er tilgængelige i egenskabseditoren i højre side, så som begrænsninger og en standardværdi, hvis ingen værdi angives. Hvert objekt i databasen vil have mange egenskaber tilknyttet, og egenskabseditoren lader dig se og redigere dem et sted.
Skifter man til datavisning, så spørges der om tabellen skal gemmes og tabeldataeditoren vises, så man manuelt kan indskrive poster, med deet er ikke særlig sjovt!
Getting The Data
With my newly created, but empty table, I needed to automatically get the data. As mentioned earlier, the data was in a single .mbox file containing all emails. Kexi supports scripts, which can be written in ecmascript (javascript), python, or a number of other languages supported by Kross, the KDE scripting framework. I chose to use the qtscript backend, which allows writing in javascript, as I am more familiar with it than python.
My script had to open the .mbox file, read it line by line, grabbing the data it needed using string manipulation, and when a full set of data was read, add it as a record to the database. Scripts not only have access to built-in methods and Kexi specific methods, but can also import libraries containing large amounts of useful functions, the most useful being the QT libraries. I will use the Core functions to have access to the filesystem using QTextStream for reading data, and the Gui functions for access to QMessageBox to be able to present errors in a dialog if they occur.
From the menu tab, this time I choose . This will launch the script editor in the central window and the property editor down the right.
A script has only a few properties, the type, and the interpreter. The interpreter I want is qtscript, and the type is Executable. An executable script is one which is meant to be run manually. A Module script is one which is meant to contain generic modules of code, accessible from other scripts, and an Object script is one which is tied to another database object such as a report.
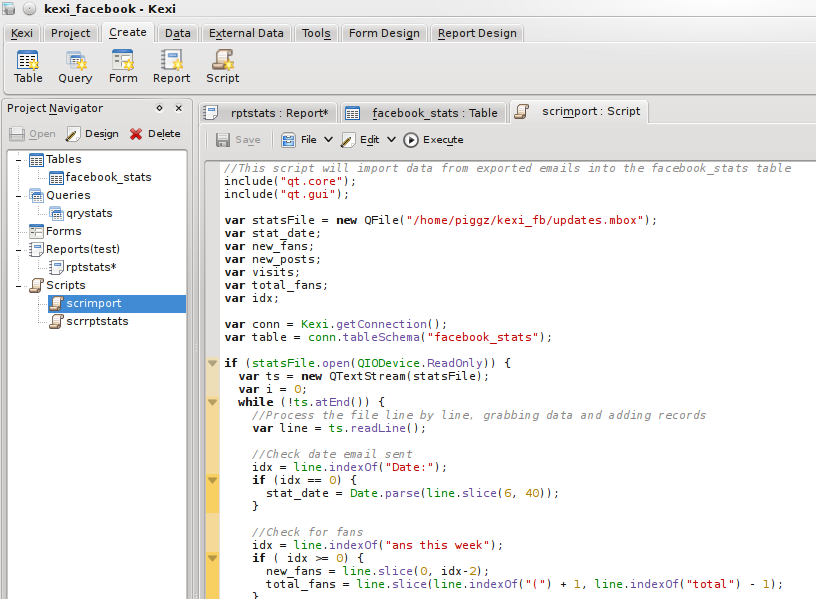
The entire script was:
//This script will import data from exported emails into the facebook_stats table
include("qt.core");
include("qt.gui");
var statsFile = new QFile("/home/piggz/kexi_fb/updates.mbox");
var stat_date;
var new_fans;
var new_posts;
var visits;
var total_fans;
var idx;
var conn = Kexi.getConnection();
var table = conn.tableSchema("facebook_stats");
if (statsFile.open(QIODevice.ReadOnly)) {
var ts = new QTextStream(statsFile);
var i = 0;
while (!ts.atEnd()) {
//Process the file line by line, grabbing data and adding records
var line = ts.readLine();
//Check date email sent
idx = line.indexOf("Date:");
if (idx == 0) {
stat_date = Date.parse(line.slice(6, 40));
}
//Check for fans
idx = line.indexOf("ans this week");
if ( idx >= 0) {
new_fans = line.slice(0, idx-2);
total_fans = line.slice(line.indexOf("(") + 1, line.indexOf("total") - 1);
}
//Check for wall posts
idx = line.indexOf("all posts");
if (idx >= 0) {
new_posts = line.slice(0, idx-2) + 0;
}
//Check for visits
idx = line.indexOf("isits to your");
if (idx >= 0) {
visits = line.slice(0,idx-2);
//Should have all the data now so insert a record
stat_date = new Date(stat_date);
var short_date = stat_date.getFullYear() + "-" + pad(stat_date.getMonth() + 1, 2) + "-" + pad(stat_date.getDate(), 2);
if (!conn.insertRecord(table, [++i, short_date, new_fans, new_posts, visits, total_fans])) {
var msg = "Cannot insert into " + table.caption() + '\n';
msg += "Date: " + stat_date.toDateString() + " " + short_date + '\n';
msg += "New Fans: " + new_fans + '\n';
msg += "Total Fans: " + total_fans + '\n';
msg += "New Posts: " + new_posts + '\n';
msg += "Visits: " + visits;
QMessageBox.information(0,"Error", msg);
}
}
}
QMessageBox.information(0, "Records Added:", i);
}
statsFile.close();
function pad(number, length) {
var str = '' + number;
while (str.length < length) {
str = '0' + str;
}
return str;
}
A possible bug in the above script is that it assumes there are no current records in the table, and creates primary keys starting at 1. It is OK to run the script once, but if it is run again, it wont overwrite records that have an ID matching what it is trying to insert. To make it more robust, it would need to first find out the current maximum of the ID field. This would be a good exercise to get used to writing scripts.
When executed from the script toolbar, the script gathered 11 records worth of data, which is visible from the Table Data View.
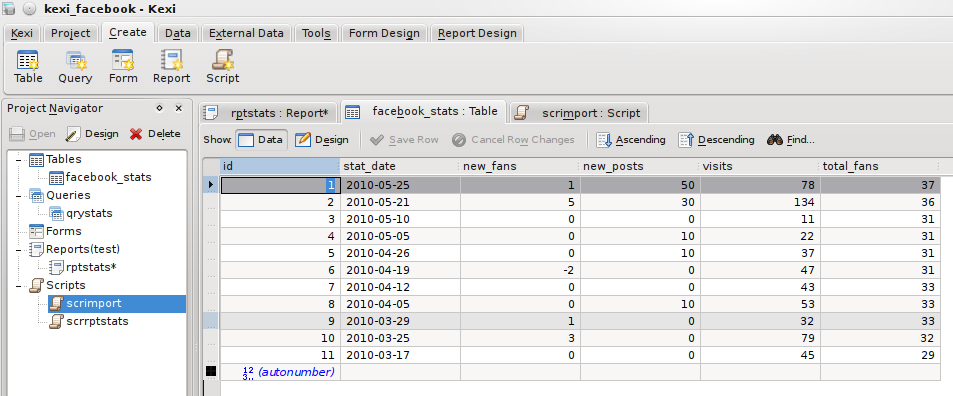
Its worth pointing out that the above script took a lot of trial and error as it is not initially obvious that it is possible to import extra libraries or use Kexi specific functions. One thing that needs to be worked on is documentation to make this easier for new users, submissions are very welcome at the KDE Userbase website.
Sort The Data, Create A Query
At the moment, the data is ordered in whatever order if came out of from KMail, I need it to be in ascending date order, so I created a query to sort it. From the tab, this time I chose . I wanted all fields except the auto-incrementing primary key, so I set it up as:
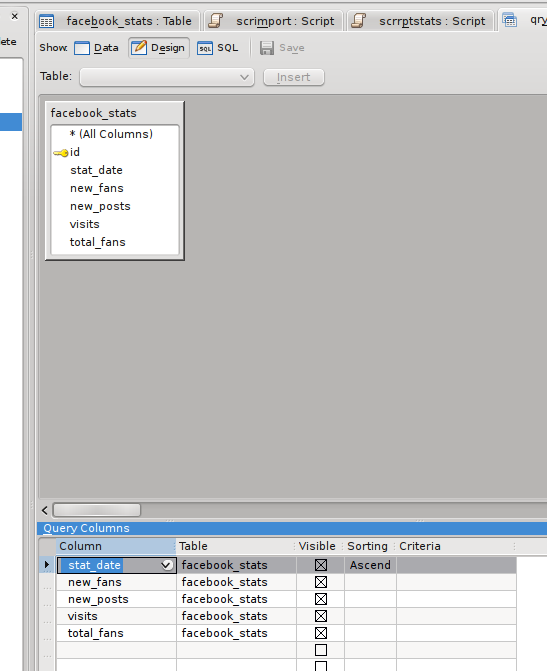
Switching to 'Data View' executes the query and displays the results:
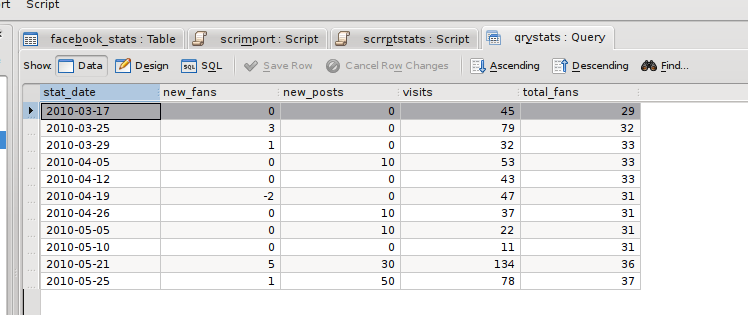
I saved the query as qryStats for use in a report.
Bringing It Together With A Report
A new feature of Kexi 2 is the report plugin. This allows reports to be designed and executed directly within Kexi using a GUI editor similar to report designers in other database systems such as Microsoft Access, Crystal Reports or Oracle Reports. In Kexi 1.6, reports were available as a separate add-on from kde-apps.org, but it did not contain as many features as the version in Kexi 2, and was not fully integrated with the application as the designer was an external program.
Reports can be printed, saved as a PDF, exported to HTML or OpenDocument Spreadsheet files or just remain in the database for live viewing. It is possible to save the report in all these formats because of the two stage generation process; reports are firsts rendered into an intermediate description, and this description is used to generate the final version in whatever format is selected. In future version, it is likely that extra formats will be supported such as OpenDocument Text and XML, suitable for further processing using XSLT.
From the tab I choose to create a blank report with a single 'Detail' section. The structure of a report is based around Sections, these can be page headers or footers, report header or footer, or Group sections where data is grouped on a field value.
Initially, all I want is a simple tabular view of the data, so all the fields will go into the detail section, apart from a header, and the field titles, which must go either in a Page Header or Report Header. From the Section Editor on the report toolbar, I added a Report Header, and using the tab on the menu bar, added fields and labels to create the report layout. From the tab on the sidebar, I set the reports data source to the qryStats query I created above. Finally I set the Control Source property of each field item to the corresponding field in the query, and the Caption of the labels appropriately. It looked like this in the end:
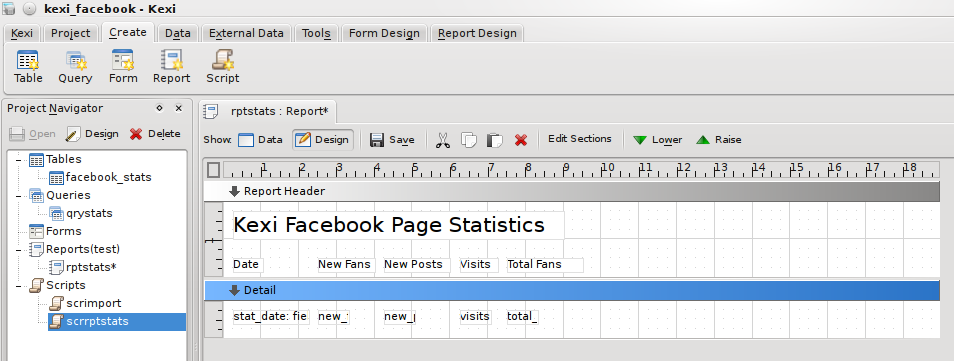
and generated a report like:
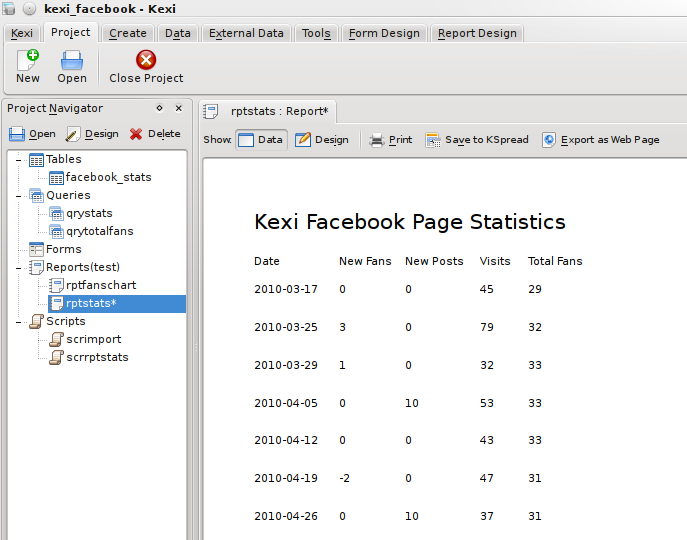
This gets the job done, but isn't quite as 'jazzed up' as I would like. Its common in desktop applications to alternate the background colour of rows to make it more obvious where each set of data begins and ends, so lets try that.
I created another script, but this time set its type to 'Object', as it is to be associated with the report object. Report scripts are event driven, that is, whenever a certain event occurs in the generation of the report, the associated code in the script is called. Report scripts use the features of Kross::Object, where each object in a report can be associated with a script object, making it more object-oriented in nature. Each script object can have its own variables and functions. Report objects can be the report itself, or any of the report sections. To make it more clear, the final script looks like:
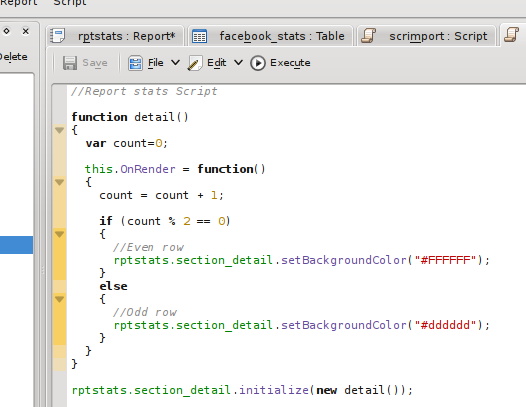
This is quite a simple script, there is an object called detail, containing a function OnRender, which will be called whenever a detail section is rendered. The function keeps track of how many times it has need called, and alternates the background colour. The final line of the script associates the detail function with the detail section of the report.
Then, in the report, I set the Interpreter Type to qtscript and the Object Script property to the name of the script. It is important that the Interpreter type of both the report and script match, otherwise the script wont be presented as an option in the Object Script list.
The generated report now looked like:
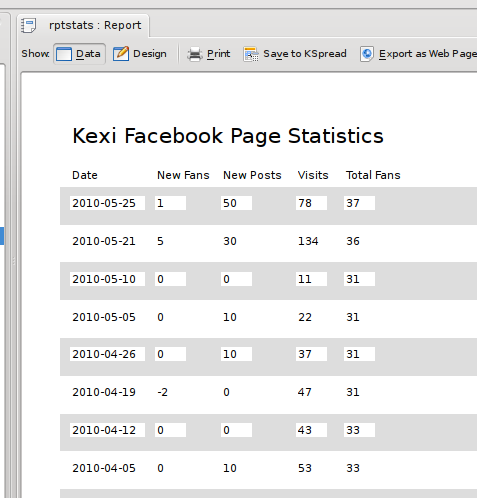
Not so great with the white background on the fields, so back in the designer, I changed the Opacity property of each of the fields to 0 to make them transparent, resulting in a more reasonable:
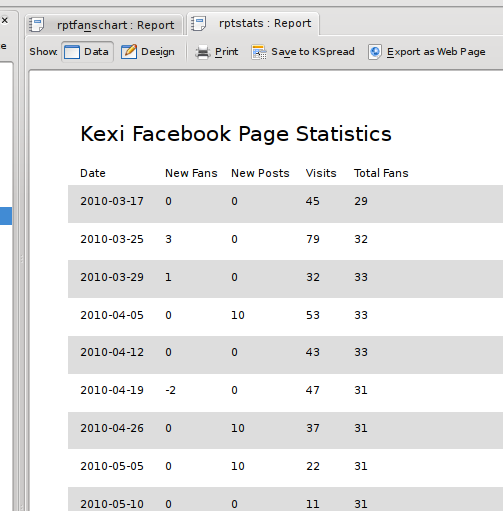
Adding Something Trendy
My final requirement at this stage was to have something more graphical; a nice chart to show the trend of fans we have over time. The report designer allows the creation of charts using the KDChart library from KDAB and is used in the KOffice program KChart. It can be quite powerful, allowing the joining of chart data to the main report data (called master-child links), but for now, all I needed was a simple, single chart. The chart object expects data in a certain format. There must be 2 or more columns of data. The first column is used for the labels on the X axis, all other columns are used as series in the chart. I started by creating a query with 2 columns, date in ascending order and total fans, then created a new report. The report itself is not based on any data, so its Data Source was left empty. An empty data source will produce a report with 1 detail section, providing an area to add a minimal set of items to a report.
In my detail section I added a chart object from the report designer toolbar and set its data source to the query I had just produced
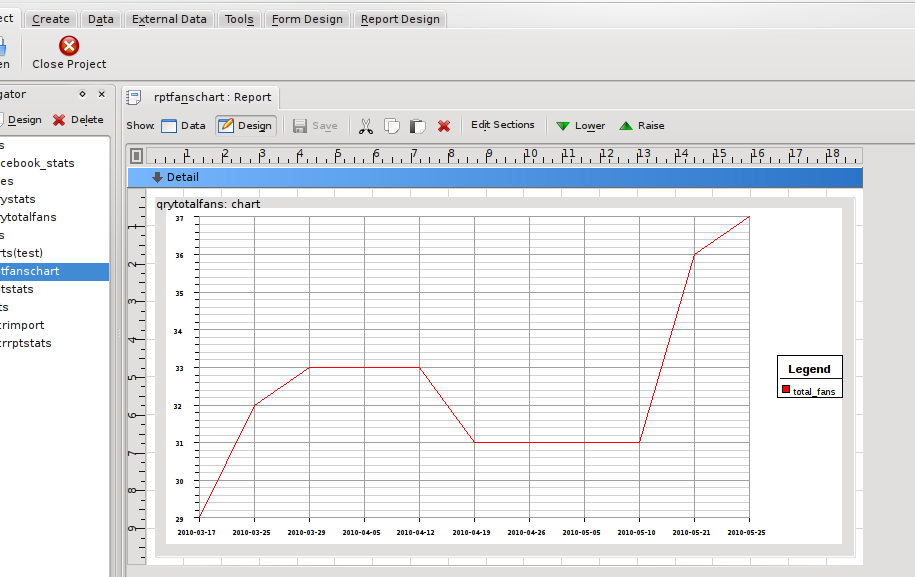
As you can see, even at design time, the chart object is able to gather data and draw a preview of the chart. Switching to the data view shows the chart without any of the extra lines and text from the designer:
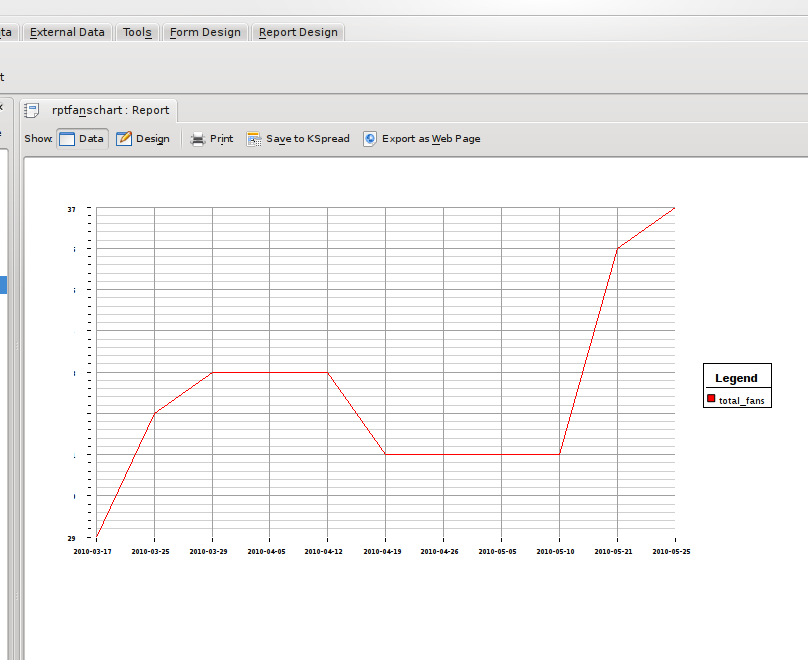
Hard Copies
When printed, both the tabular report and chart report look as they do in the Data view. When printed using the PDF printer option in KDE, the chart even retains all its detail, as it is not converted to a bitmap, but saved as lines which makes it completely zoomable!
Saving the tabular report as a HTML document produces 2 options, saving as a table, or using CSS. The table option produces a HTML file where the text from each field in a report is saved as a table cell, and each section is a row. The CSS options uses the
The tabular report also exports nicely into an OpenDocument Spreadsheet file for use in either KSpread or OpenOffice:
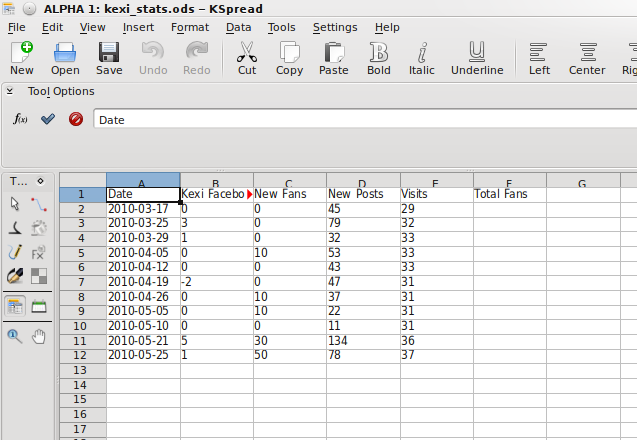
As you can see from the image, one problem is that the title of the report has taken a cell with the other field headings, this is because it is in the same section and easily fixed by putting the title into a separate section such as a Page Header.
That concludes this write-up on some of the features of Kexi in KOffice 2.2. Find out what else is possible by giving it a go and if you can, please contribute more documentation @ [4], or join the team by dropping into #kexi or #koffice on freenode IRC.
Resources


