KWord/Manual/IntroGUI: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Marked this version for translation |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
== Introducing KWord's Graphical User Interface == | == Introducing KWord's Graphical User Interface == <!--T:1--> | ||
<!--T:2--> | |||
'''DON`T PANIC!!''' | '''DON`T PANIC!!''' | ||
<!--T:3--> | |||
The '''KWord GUI''' (as well as those of other KOffice applications) is flexible, simple and extensible at the same time. Such an interface reflects the ideas of deep integration of different applications in office suite as well as modular structure of both ''KOffice'' and '''KWord''' as one of its parts. | The '''KWord GUI''' (as well as those of other KOffice applications) is flexible, simple and extensible at the same time. Such an interface reflects the ideas of deep integration of different applications in office suite as well as modular structure of both ''KOffice'' and '''KWord''' as one of its parts. | ||
== Key parts of the KWord GUI == | == Key parts of the KWord GUI == <!--T:4--> | ||
<!--T:5--> | |||
[[Image:Interface_explanation.png|center|500px|thumb]] | [[Image:Interface_explanation.png|center|500px|thumb]] | ||
<!--T:6--> | |||
As we see from the picture above, the key components of KWord GUI are the following: | As we see from the picture above, the key components of KWord GUI are the following: | ||
* Menus | * Menus | ||
| Line 18: | Line 22: | ||
* Toolbars | * Toolbars | ||
<!--T:7--> | |||
Menus always stay at the same place, while ''dockers'' and ''toolbars'' are dynamic pieces of the '''KWord GUI''' that can be dragged around the whole interface, float free or be grounded/grouped at any one of 4 edges of your screen. This allows for building the interface which You need, not the choice of somebody who thinks he is to define what ''Your'' word processor / working style / thinking should be like. | Menus always stay at the same place, while ''dockers'' and ''toolbars'' are dynamic pieces of the '''KWord GUI''' that can be dragged around the whole interface, float free or be grounded/grouped at any one of 4 edges of your screen. This allows for building the interface which You need, not the choice of somebody who thinks he is to define what ''Your'' word processor / working style / thinking should be like. | ||
<!--T:8--> | |||
The flexibility of '''Kword GUI''' allows You to make Your word processor look, for example, like this: | The flexibility of '''Kword GUI''' allows You to make Your word processor look, for example, like this: | ||
<!--T:9--> | |||
[[File:Interface.png|center|500px|thumb]] | [[File:Interface.png|center|500px|thumb]] | ||
<!--T:10--> | |||
Such an interface setup allows, for example, to use '''KWord''' if you have a KDE panel popping up from the right side of your screen as your mouse approaches it. If you have set up your workspace like that sometimes your panel might be making it hard for you to get to your dockers. | Such an interface setup allows, for example, to use '''KWord''' if you have a KDE panel popping up from the right side of your screen as your mouse approaches it. If you have set up your workspace like that sometimes your panel might be making it hard for you to get to your dockers. | ||
===Menus=== | ===Menus=== <!--T:11--> | ||
<!--T:12--> | |||
Menus are Your terra firma (firm ground under Your feet) of the '''KWord GUI''' - all the applications' functions are accessible from there and menus are always visible to the user. In some cases the user may find it to be the most convenient way to use menus only (very small screen estate), but usually they are used in combination with dockers and toolbars. | Menus are Your terra firma (firm ground under Your feet) of the '''KWord GUI''' - all the applications' functions are accessible from there and menus are always visible to the user. In some cases the user may find it to be the most convenient way to use menus only (very small screen estate), but usually they are used in combination with dockers and toolbars. | ||
<!--T:13--> | |||
Most users prefer to use dockers and toolbars as a quick visual access for the functions they use frequently and go to the menu for less used functions. For example, making text bold or italic or selecting font is in most cases more frequently used then say, the frameset properties and it makes more sense to access the latter from the menu. | Most users prefer to use dockers and toolbars as a quick visual access for the functions they use frequently and go to the menu for less used functions. For example, making text bold or italic or selecting font is in most cases more frequently used then say, the frameset properties and it makes more sense to access the latter from the menu. | ||
===Toolbars=== | ===Toolbars=== <!--T:14--> | ||
<!--T:15--> | |||
Oooh, these mighty '''KWord toolbars''' {{smiley}} | Oooh, these mighty '''KWord toolbars''' {{smiley}} | ||
===Dockers=== | ===Dockers=== <!--T:16--> | ||
<!--T:17--> | |||
'''KWord''' interface, as well as the interface of any KOffice application is built around the concept of ''Dockers''. A ''Docker'' is, essentially a '''KOffice GUI''' ''widget'' that unites certain related functions. For example, "color chooser" docker allows user to choose a color of editable object, "Add Shape" docker allows user to add different shapes (text, images, etc) to their '''KWord''' document. | '''KWord''' interface, as well as the interface of any KOffice application is built around the concept of ''Dockers''. A ''Docker'' is, essentially a '''KOffice GUI''' ''widget'' that unites certain related functions. For example, "color chooser" docker allows user to choose a color of editable object, "Add Shape" docker allows user to add different shapes (text, images, etc) to their '''KWord''' document. | ||
<!--T:18--> | |||
Every docker allows for certain editing functionality in '''KWord'''. ''Since the dockers can be easily turned on and off, grouped, they allow the GUI to be set up so that only the functions the user actually uses/needs are visible in KWord GUI.'' | Every docker allows for certain editing functionality in '''KWord'''. ''Since the dockers can be easily turned on and off, grouped, they allow the GUI to be set up so that only the functions the user actually uses/needs are visible in KWord GUI.'' | ||
<!--T:19--> | |||
[[File:Docker1.png|center|thumb|500px|''KWord with dockers on the right side'']] | [[File:Docker1.png|center|thumb|500px|''KWord with dockers on the right side'']] | ||
==Using Menus== | ==Using Menus== <!--T:20--> | ||
==Using Toolbars== | ==Using Toolbars== <!--T:21--> | ||
==Using Dockers== | ==Using Dockers== <!--T:22--> | ||
===List of KWord dockers=== | ===List of KWord dockers=== <!--T:23--> | ||
<!--T:24--> | |||
* Toolbox | * Toolbox | ||
* Tool Options | * Tool Options | ||
| Line 67: | Line 82: | ||
* Shadow properties | * Shadow properties | ||
===Governing dockers (turning on and off)=== | ===Governing dockers (turning on and off)=== <!--T:25--> | ||
<!--T:26--> | |||
Of course, each user has different requirements of the word processing tool. Especially when the tool is that versatile as '''KWord''' is. | Of course, each user has different requirements of the word processing tool. Especially when the tool is that versatile as '''KWord''' is. | ||
<!--T:27--> | |||
A nice example of that is its ''RDF'' functions. This is used, for example, to integrate someone's contacts into your document, so that when they are changed, say in your addressbook they are changed in your document. A cool feature, right? Sure, but some people do not need it at all. They are happy with typing and making letters big/small and bold/regular. | A nice example of that is its ''RDF'' functions. This is used, for example, to integrate someone's contacts into your document, so that when they are changed, say in your addressbook they are changed in your document. A cool feature, right? Sure, but some people do not need it at all. They are happy with typing and making letters big/small and bold/regular. | ||
<!--T:28--> | |||
We easily came to a conclusion that not really everybody needs to have all the dockers in their '''KWord''' interface. It is always better to have some more free space for some other dockers. | We easily came to a conclusion that not really everybody needs to have all the dockers in their '''KWord''' interface. It is always better to have some more free space for some other dockers. | ||
<!--T:29--> | |||
Since dockers reflect the modularity of KOffice and '''KWord''' their number is constantly growing as is the number of tools and plugins which are available for '''KWord'''. And this is the very point where we understand that we need to manage them somehow. Especially if You have a not-so-new notebook with limited screen width. | Since dockers reflect the modularity of KOffice and '''KWord''' their number is constantly growing as is the number of tools and plugins which are available for '''KWord'''. And this is the very point where we understand that we need to manage them somehow. Especially if You have a not-so-new notebook with limited screen width. | ||
<!--T:30--> | |||
''So, how can You get dockers located on screen in order that is good for you?'' | ''So, how can You get dockers located on screen in order that is good for you?'' | ||
<!--T:31--> | |||
Simple: | Simple: | ||
* Switch off the unnecessary dockers | * Switch off the unnecessary dockers | ||
| Line 86: | Line 107: | ||
* Group them (probably the most important) | * Group them (probably the most important) | ||
<!--T:32--> | |||
''THE DOCKERS CAN BE HIDDEN BY PRESSING Ctrl+H, starting from KOffice 2.3'' | ''THE DOCKERS CAN BE HIDDEN BY PRESSING Ctrl+H, starting from KOffice 2.3'' | ||
===Grouping dockers=== | ===Grouping dockers=== <!--T:33--> | ||
<!--T:34--> | |||
[[Category:Office]] | [[Category:Office]] | ||
</translate> | </translate> | ||
Revision as of 12:50, 20 July 2011
Introducing KWord's Graphical User Interface
DON`T PANIC!!
The KWord GUI (as well as those of other KOffice applications) is flexible, simple and extensible at the same time. Such an interface reflects the ideas of deep integration of different applications in office suite as well as modular structure of both KOffice and KWord as one of its parts.
Key parts of the KWord GUI
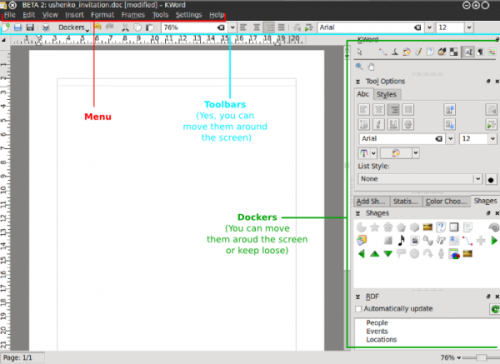
As we see from the picture above, the key components of KWord GUI are the following:
- Menus
- Dockers
- Toolbars
Menus always stay at the same place, while dockers and toolbars are dynamic pieces of the KWord GUI that can be dragged around the whole interface, float free or be grounded/grouped at any one of 4 edges of your screen. This allows for building the interface which You need, not the choice of somebody who thinks he is to define what Your word processor / working style / thinking should be like.
The flexibility of Kword GUI allows You to make Your word processor look, for example, like this:
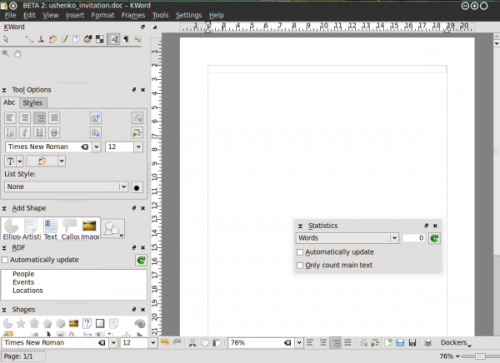
Such an interface setup allows, for example, to use KWord if you have a KDE panel popping up from the right side of your screen as your mouse approaches it. If you have set up your workspace like that sometimes your panel might be making it hard for you to get to your dockers.
Menus
Menus are Your terra firma (firm ground under Your feet) of the KWord GUI - all the applications' functions are accessible from there and menus are always visible to the user. In some cases the user may find it to be the most convenient way to use menus only (very small screen estate), but usually they are used in combination with dockers and toolbars.
Most users prefer to use dockers and toolbars as a quick visual access for the functions they use frequently and go to the menu for less used functions. For example, making text bold or italic or selecting font is in most cases more frequently used then say, the frameset properties and it makes more sense to access the latter from the menu.
Toolbars
Oooh, these mighty KWord toolbars ![]()
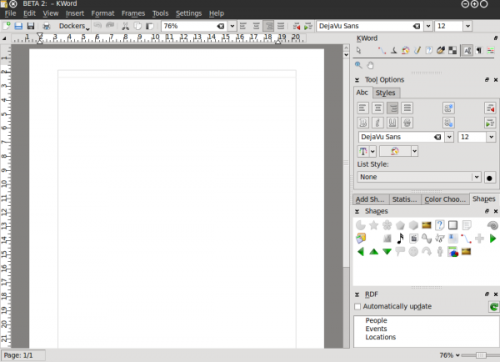
Dockers
KWord interface, as well as the interface of any KOffice application is built around the concept of Dockers. A Docker is, essentially a KOffice GUI widget that unites certain related functions. For example, "color chooser" docker allows user to choose a color of editable object, "Add Shape" docker allows user to add different shapes (text, images, etc) to their KWord document.
Every docker allows for certain editing functionality in KWord. Since the dockers can be easily turned on and off, grouped, they allow the GUI to be set up so that only the functions the user actually uses/needs are visible in KWord GUI.
Using Menus
Using Toolbars
Using Dockers
List of KWord dockers
- Toolbox
- Tool Options
- RDF
- Add shape
- Statistics
- Color chooser
- Shapes
- Scripts
- Shape properties
- Shadow properties
Governing dockers (turning on and off)
Of course, each user has different requirements of the word processing tool. Especially when the tool is that versatile as KWord is.
A nice example of that is its RDF functions. This is used, for example, to integrate someone's contacts into your document, so that when they are changed, say in your addressbook they are changed in your document. A cool feature, right? Sure, but some people do not need it at all. They are happy with typing and making letters big/small and bold/regular.
We easily came to a conclusion that not really everybody needs to have all the dockers in their KWord interface. It is always better to have some more free space for some other dockers.
Since dockers reflect the modularity of KOffice and KWord their number is constantly growing as is the number of tools and plugins which are available for KWord. And this is the very point where we understand that we need to manage them somehow. Especially if You have a not-so-new notebook with limited screen width.
So, how can You get dockers located on screen in order that is good for you?
Simple:
- Switch off the unnecessary dockers
- Switch on the needed ones (yes, those you personally need, not those someone said must be in a word processor)
- Change the screen edge to suit the way you work
- Make dockers independent
- Group them (probably the most important)
THE DOCKERS CAN BE HIDDEN BY PRESSING Ctrl+H, starting from KOffice 2.3
