Step/da: Difference between revisions
(Importing a new version from external source) |
(Importing a new version from external source) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
==Beskrivelse== | ==Beskrivelse== | ||
'''Step''' | '''Step''' er en interaktiv fysiksimulator. Den virker således: du placerer nogle legemer på scenen, tilføjer nogle kræfter så som gravitation eller fjedre og klikker så <menuchoice>Simulate</menuchoice>; '''Step''' viser dig så, hvordan din scene udvikler sig i overensstemmelse med fysikkens love. Du kan ændre alle legemernes og kræfternes egenskaber (selv under en simulering) og se, hvordan det påvirker dir eksperiment. Med '''Step''' kan du ikke bare lære fysik, du kan fornemme, hvordan det virker! | ||
==Features== | ==Features== | ||
Revision as of 18:45, 5 October 2010
Hjem » Programmer » Uddannelse » Step

|
Step er en interaktiv fysiksimulator. Den lader dig udforske den fysiske verden gennem simulationer Den er en del af KDE Education Project. |
Beskrivelse
Step er en interaktiv fysiksimulator. Den virker således: du placerer nogle legemer på scenen, tilføjer nogle kræfter så som gravitation eller fjedre og klikker så ; Step viser dig så, hvordan din scene udvikler sig i overensstemmelse med fysikkens love. Du kan ændre alle legemernes og kræfternes egenskaber (selv under en simulering) og se, hvordan det påvirker dir eksperiment. Med Step kan du ikke bare lære fysik, du kan fornemme, hvordan det virker!
Features
- Classical mechanical simulation in two dimensions
- Particles, springs with dumping, gravitational and coulomb forces
- Rigid bodies
- Collision detection (currently only discrete) and handling
- Soft (deformable) bodies simulated as user-editable particles-springs system, sound waves
- Molecular dynamics (currently using Lennard-Jones potential): gas and liquid, condensation and evaporation, calculation of macroscopic quantities and their variances
- Units conversion and expression calculation: you can enter something like "(2 days + 3 hours) * 80 km/h" and it will be accepted as distance value (requires libqalculate)
- Errors calculation and propagation: you can enter values like "1.3 ± 0.2" for any property and errors for all dependent properties will be calculated using statistical formulas
- Solver error estimation: errors introduced by the solver is calculated and added to user-entered errors
- Several different solvers: up to 8th order, explicit and implicit, with or without adaptive timestep (most of the solvers require GSL library)
- Controller tool to easily control properties during simulation (even with custom keyboard shortcuts)
- Tools to visualize results: graph, meter, tracer
- Context information for all objects, integrated wikipedia browser
- Collection of example experiments, more can be downloaded with KNewStuff2
- Integrated tutorials
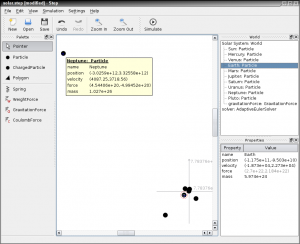
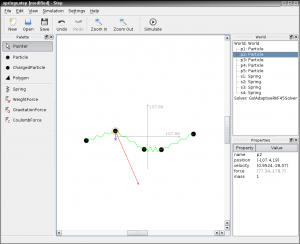
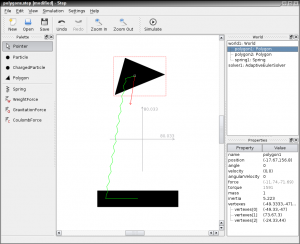
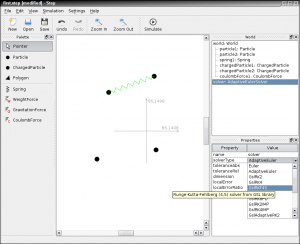
Screenshots
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Documentation
Weblinks
StepCore Library
StepCore is the physical simulation library on which Step is based. It can be used without Step for complex simulations which require coding or in other software which require physical simulation functionality. It is designed in order to be extensible, tunable and to provide accurate simulation.
You can find more information about the StepCore library on techbase.kde.org.
