KDevelop5/Manual/Working with version control systems/da: Difference between revisions
Importing a new version from external source |
Created page with "===Git===" |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Arbejdet med versionskontrolsystemer == | == Arbejdet med versionskontrolsystemer == | ||
Hvis du arbejder med store projekter, så bliver kildekoden sandsynligvis håndteret af et versionskontrolsystem så som [http://subversion.apache.org subversion] eller [http://git-scm.com/ git]. Det følgende er skrevet med '''subversion''' i tankerne, men vil være lige så sandt, hvis du bruger '''git''' eller et andet understøttet versionskontrolsystem. | |||
===Subversion=== | |||
Bemærk først, at hvis mappen, som projektet er placeret i er under versionskontrol, så vil '''KDevelop''' automatisk bemærke det. Med andre ord behøver du ikke at bede '''KDevelop''' om at tjekke en kopi ud, når du opsætter dit projekt. Det er i orden at dirigere '''KDevelop''' til en mappe, til hvilken du tidligere har tjekket en kopi fra et arkiv ud. Hvis du har en mappe under versionskontrol, så åbn værktøjsvisningen '''Projekter'''. Der er flere ting du kan gøre: | |||
* | * Hvis din mappe er blevet forældet, så kan du opdatere den fra arkivet: Højre-klik på projektets navn og vælg <menuchoice>Subversion</menuchoice> og vælg <menuchoice>Opdatér</menuchoice>. Dette vil synkronisere alle filerne i dette projekt med arkivet. | ||
* Hvis du ønsker at begrænse denne handling til individuelle undermapper eller filer, så udvid projektets trævisning til det niveau, du ønsker, højreklik på undermappen eller filen og gør det samme som ovenfor. | |||
[[Image:kdevelop-8.png|thumb|600px]] | [[Image:kdevelop-8.png|thumb|600px]] | ||
* | * Hvis du har redigeret en eller flere filer, så udvid projektvisningen til mappen, hvor disse filer findes og højreklik på den. Menupunktet <menuchoice>Subversion</menuchoice> giver dig forskellige muligheder. Vælg <menuchoice>Sammenlign med Base...</menuchoice> for at se forskellene imellem den version, som du har redigeret og den version, som er i det arkiv, som du tidligere tjekkede projektet ud fra ("revisionsbasen"). Det resulterer i en visning af forskellene for alle filerne i denne mappe. | ||
* Hvis du kun har redigeret en enkelt fil, så kan du også få menuen <menuchoice>Subversion</menuchoice> for denne fil ved simpelthen at højreklikke på det tilsvarende filnavn i projektvisningen. Du kan også bare højreklikke i den editorvisning, som filen blev redigeret i for at få denne menu frem. | |||
* Hvis du tjekke en eller flere redigerede filer ind, så højreklik enten på en individuel fil, en mappe eller hele projektet og vælg <menuchoice>Subversion -> Commit</menuchoice>. Derved havner du i tilstanden <menuchoice>Eftersyn</menuchoice>, den tredje tilstand ved siden af <menuchoice>Kode</menuchoice> og <menuchoice>Fejlsøgning</menuchoice>, som du finder i øverste højre hjørne af '''KDevelops''' hovedvindue. Billedet til højre viser, hvordan det ser ud. I tilstanden <menuchoice>Eftersyn</menuchoice> viser den øverste del forskelle for hele undermappen eller projektet og for hver enkelt ændret fil med ændringerne fremhævet (se de forskellige faneblade i denne del af vinduet). Som udgangspunkt er alle ændrede filer del af det "changeset", som du er ved at committe, men du kan fravælge nogle af filerne, hvis deres ændringer ikke er relaterede til det, som du ønsker at committe. I eksemplet til højre har jeg for eksempel fravalgt <code>step-32.cc</code> og <code>step-32.prm</code>, fordi ændringerne i disse filer ikke har noget at gøre med de andre ændringer, som jeg lavede i projektet og jeg ikke ønsker at tjekke dem ind endnu (det vil jeg måske gøre senere i et separat commit). Efter at have efterset ændringerne kan du skrive en commit-besked i tekstboksen og klikke på <menuchoice>Commit</menuchoice> til højre for at sende dem af sted. | |||
* Hvis du blot ønsket at committe en enkelt fil, så kan du — ligesom ved visning af forskelle — også højreklikke i editorvinduet og vælge menuen <menuchoice>Subversion -> Commit</menuchoice>. | |||
===Git=== | |||
[[File:Kdevelop-git-options.png|300px|thumb|right]] Since [http://git-scm.com/ git] is becoming more and more popular with companies programmers, let us look at the options for git. Whether you right-click on the project name or on an individual file, one of the menu choices it gives you is <menuchoice>Git</menuchoice>. When clicked it produces the submenu shown on the right with some of the more common git commands. | |||
;Commit | |||
: Commit your changes to the local repository with an optional message describing the changes made. | |||
;Push | |||
: Update the remote repository. | |||
;Pull | |||
: Fetch from and integrate with the local repository from the remote repository. | |||
;Add | |||
: Add the file to the list of files to be committed when you perform the commit. This can be used as many times as needed before the commit. | |||
;Revert | |||
: Reverse an earlier commit due to a commit error or a patch that is creating a problem. | |||
;Search History | |||
: Search history pulls up a dialog that displays the log of the commits along with the commit message and a list of files affected. | |||
;Annotation | |||
: Annotates each line in the given file with commit information. | |||
;Show Differences | |||
: Shows the differences of a patch. | |||
;Branches | |||
: Opens a dialog that shows the current branches as well as a search box, and buttons for the following branch actions: create, delete, rename, compare, checkout, and merge. | |||
;Rebase | |||
: Opens a dialog to select the branch to rebase to. | |||
;Stash Manager | |||
: Opens a dialog displaying a list of stashes that have been pushed with buttons to determine what to do next. The buttons have the following actions: | |||
*Show: Shows the selected stash as a diff and switches to diff view | |||
*Apply: Applies the stash but does not remove the stash | |||
*Pop: Applies the stash and removes it from the Stash Manager | |||
*Branch: Opens a dialog for a branch name to create with the stash | |||
* | *Drop: Deletes the stash | ||
* | *Close: Closes the Stash Manager | ||
;Push Stash | |||
: Save your local modifications to the current working branch to a new stash entry and roll them back to HEAD. The <message> part is optional and gives the stash a description. | |||
;Pop Stash | |||
: Remove a single stash from the stash list and apply it on top of the current working tree, i.e., do the opposite operation of git stash push. The working directory must match the index. | |||
{{Prevnext2 | {{Prevnext2 | ||
| prevpage=Special:MyLanguage/KDevelop5/Manual/Debugging_programs | nextpage=Special:MyLanguage/KDevelop5/Manual/Customizing KDevelop | | prevpage=Special:MyLanguage/KDevelop5/Manual/Debugging_programs | nextpage=Special:MyLanguage/KDevelop5/Manual/Customizing KDevelop | ||
| prevtext= | | prevtext=Fejlsøgning af programmer | nexttext=Tilpasning af KDevelop | ||
| index=Special:MyLanguage/KDevelop5/Manual | indextext= | | index=Special:MyLanguage/KDevelop5/Manual | indextext=Indholdsfortegnelse | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Udvikling/da]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:59, 14 November 2022
Arbejdet med versionskontrolsystemer
Hvis du arbejder med store projekter, så bliver kildekoden sandsynligvis håndteret af et versionskontrolsystem så som subversion eller git. Det følgende er skrevet med subversion i tankerne, men vil være lige så sandt, hvis du bruger git eller et andet understøttet versionskontrolsystem.
Subversion
Bemærk først, at hvis mappen, som projektet er placeret i er under versionskontrol, så vil KDevelop automatisk bemærke det. Med andre ord behøver du ikke at bede KDevelop om at tjekke en kopi ud, når du opsætter dit projekt. Det er i orden at dirigere KDevelop til en mappe, til hvilken du tidligere har tjekket en kopi fra et arkiv ud. Hvis du har en mappe under versionskontrol, så åbn værktøjsvisningen Projekter. Der er flere ting du kan gøre:
- Hvis din mappe er blevet forældet, så kan du opdatere den fra arkivet: Højre-klik på projektets navn og vælg og vælg . Dette vil synkronisere alle filerne i dette projekt med arkivet.
- Hvis du ønsker at begrænse denne handling til individuelle undermapper eller filer, så udvid projektets trævisning til det niveau, du ønsker, højreklik på undermappen eller filen og gør det samme som ovenfor.
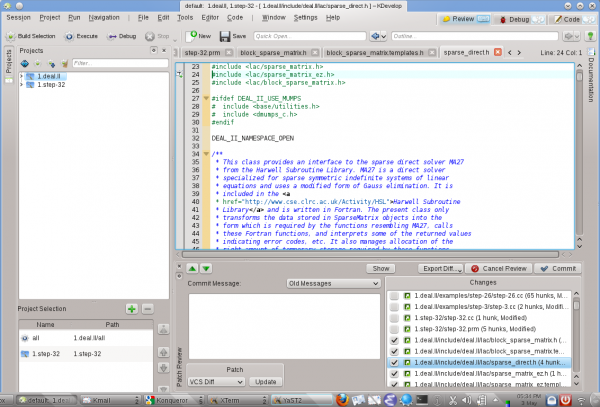
- Hvis du har redigeret en eller flere filer, så udvid projektvisningen til mappen, hvor disse filer findes og højreklik på den. Menupunktet giver dig forskellige muligheder. Vælg for at se forskellene imellem den version, som du har redigeret og den version, som er i det arkiv, som du tidligere tjekkede projektet ud fra ("revisionsbasen"). Det resulterer i en visning af forskellene for alle filerne i denne mappe.
- Hvis du kun har redigeret en enkelt fil, så kan du også få menuen for denne fil ved simpelthen at højreklikke på det tilsvarende filnavn i projektvisningen. Du kan også bare højreklikke i den editorvisning, som filen blev redigeret i for at få denne menu frem.
- Hvis du tjekke en eller flere redigerede filer ind, så højreklik enten på en individuel fil, en mappe eller hele projektet og vælg . Derved havner du i tilstanden , den tredje tilstand ved siden af og , som du finder i øverste højre hjørne af KDevelops hovedvindue. Billedet til højre viser, hvordan det ser ud. I tilstanden viser den øverste del forskelle for hele undermappen eller projektet og for hver enkelt ændret fil med ændringerne fremhævet (se de forskellige faneblade i denne del af vinduet). Som udgangspunkt er alle ændrede filer del af det "changeset", som du er ved at committe, men du kan fravælge nogle af filerne, hvis deres ændringer ikke er relaterede til det, som du ønsker at committe. I eksemplet til højre har jeg for eksempel fravalgt
step-32.ccogstep-32.prm, fordi ændringerne i disse filer ikke har noget at gøre med de andre ændringer, som jeg lavede i projektet og jeg ikke ønsker at tjekke dem ind endnu (det vil jeg måske gøre senere i et separat commit). Efter at have efterset ændringerne kan du skrive en commit-besked i tekstboksen og klikke på til højre for at sende dem af sted.
- Hvis du blot ønsket at committe en enkelt fil, så kan du — ligesom ved visning af forskelle — også højreklikke i editorvinduet og vælge menuen .
Git
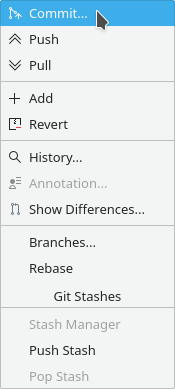
Since git is becoming more and more popular with companies programmers, let us look at the options for git. Whether you right-click on the project name or on an individual file, one of the menu choices it gives you is . When clicked it produces the submenu shown on the right with some of the more common git commands.
- Commit
- Commit your changes to the local repository with an optional message describing the changes made.
- Push
- Update the remote repository.
- Pull
- Fetch from and integrate with the local repository from the remote repository.
- Add
- Add the file to the list of files to be committed when you perform the commit. This can be used as many times as needed before the commit.
- Revert
- Reverse an earlier commit due to a commit error or a patch that is creating a problem.
- Search History
- Search history pulls up a dialog that displays the log of the commits along with the commit message and a list of files affected.
- Annotation
- Annotates each line in the given file with commit information.
- Show Differences
- Shows the differences of a patch.
- Branches
- Opens a dialog that shows the current branches as well as a search box, and buttons for the following branch actions: create, delete, rename, compare, checkout, and merge.
- Rebase
- Opens a dialog to select the branch to rebase to.
- Stash Manager
- Opens a dialog displaying a list of stashes that have been pushed with buttons to determine what to do next. The buttons have the following actions:
- Show: Shows the selected stash as a diff and switches to diff view
- Apply: Applies the stash but does not remove the stash
- Pop: Applies the stash and removes it from the Stash Manager
- Branch: Opens a dialog for a branch name to create with the stash
- Drop: Deletes the stash
- Close: Closes the Stash Manager
- Push Stash
- Save your local modifications to the current working branch to a new stash entry and roll them back to HEAD. The <message> part is optional and gives the stash a description.
- Pop Stash
- Remove a single stash from the stash list and apply it on top of the current working tree, i.e., do the opposite operation of git stash push. The working directory must match the index.
