Amarok/Manual/Organization/Collection/ExternalDatabase/cs: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Created page with "'''Amarok''' 2.2 a novější podporuje jako podpůrnou vrstvu vnější databázi '''MySQL'''." |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==== Vnější databáze ==== | ==== Vnější databáze ==== | ||
'''Amarok''' 2.2 | '''Amarok''' 2.2 a novější podporuje jako podpůrnou vrstvu vnější databázi '''MySQL'''. | ||
===== Nastavit server ===== | ===== Nastavit server ===== | ||
Revision as of 11:16, 2 September 2013
Vnější databáze
Amarok 2.2 a novější podporuje jako podpůrnou vrstvu vnější databázi MySQL.
Nastavit server
Instalovat server MySQL
First you need to install an MySQL server. On Debian-based distributions like Ubuntu you can use
sudo apt-get install mysql-server mysql-client
to install it. You will be asked to specify a password for the root-account for the database. The mysql-client package is needed in order to execute some of the commands in this document, but it's not fundamental to the use of Amarok.
Nastavit databázi
Připojit k místní databázi pomocí
mysql -u root -p
Budete vyzván k zadání hesla pro uživatele root MySQL. Dostanete výzvu
mysql>
.
Vytvořte nového uživatele amarokuser s heslem amarokpass pomocí příkazu
CREATE USER ''''amarokuser''''@''''localhost'''' IDENTIFIED BY ''''amarokpass'''';
. Amarok potřebuje svou vlastní databázi, která je vytvořena
CREATE DATABASE '''amarokdb''';
Dejte novému uživateli přístup k databázi zadáním příkazu
GRANT ALL ON '''amarokdb'''.* TO ''''amarokuser''''@''''%'''' IDENTIFIED BY ''''amarokpass'''';
, kde % je zástupný symbol kvůli povolení připojení k databázi všem hostům . Nyní použijte příkaz
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
k znovunahrání různých vnitřních vyrovnávacích pamětí používaných MySQL. Na závěr
exit
closes the MySQL prompt.
By default the server can only be accessed by the local host. To change this you need to edit the file /etc/mysql/my.cnf and adjust the address near bind-address to the one your server listens on the network. 0.0.0.0 listens on all interfaces. After that you need to restart the server using
sudo service mysql restart
Nastavit klienta
Open the configuration dialog by clicking . Enable the checkbox and enter the user data.
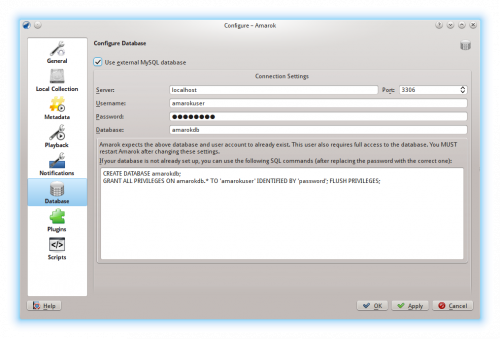
Musíte Amarok spustit znovu, aby se změny mohly projevit.
Přestěhování z MySQL Embedded do MySQL Server
If you want to maintain the statistics, etc. that you have in the embedded MySQL database from before Amarok 2.2, you can do the following: First, start Amarok 2.2+ at least once to give the database a chance to update to the latest schema version.
Next, kill the running MySQL service
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
and start a MySQL daemon from your ~/.kde4/share/apps/amarok directory (--defaults-file MUST be the first option!):
/usr/sbin/mysqld --defaults-file=`pwd`/my.cnf --default-storage-engine=MyISAM --datadir=`pwd`/mysqle --socket=`pwd`/sock --skip-grant-tables
The skip-grant-tables means you can use any password or username to connect to it. 'localhost' will not work, the MySQL client will try to use a Unix socket. Using 127.0.0.1 as the host makes it work. Some systems may restrict this access through apparmor or SELinux. They can be temporarily disabled with
sudo /etc/init.d/apparmor stop
Now, run mysqldump, passing in the -S option to specify the local socket. This will dump your old embedded DB out to a SQL file.
mysqldump -S sock amarok > amarok.mysql
You can then restart your MySQL service and load this SQL file into your MySQL server. You'll have needed to already run the GRANT statement above and create an Amarok database ("CREATE DATABASE amarok;"):
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
mysql -u amarokuser -p amarok < amarok.mysql

