Step/it: Difference between revisions
Importing a new version from external source |
Importing a new version from external source |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
'''Step''' è un simulatore fisico interattivo. Funziona così: posiziona alcuni corpi nella scena, aggiungi alcune forze come gravità o molle, poi fai clic su <menuchoice>Simula</menuchoice> e '''Step''' ti mostrerà come la scena evolve secondo le leggi della fisica. Puoi modificare ogni proprietà dei corpi/forze nel tuo esperimento (anche durante la simulazione) e vedere come questo modificherà il risultato dell'esperimento. Con '''Step''' puoi non solo imparare, ma anche "sentire" come funziona la fisica! | '''Step''' è un simulatore fisico interattivo. Funziona così: posiziona alcuni corpi nella scena, aggiungi alcune forze come gravità o molle, poi fai clic su <menuchoice>Simula</menuchoice> e '''Step''' ti mostrerà come la scena evolve secondo le leggi della fisica. Puoi modificare ogni proprietà dei corpi/forze nel tuo esperimento (anche durante la simulazione) e vedere come questo modificherà il risultato dell'esperimento. Con '''Step''' puoi non solo imparare, ma anche "sentire" come funziona la fisica! | ||
== | ==Caratteristiche== | ||
* Classical mechanical simulation in two dimensions | * Classical mechanical simulation in two dimensions | ||
Revision as of 11:08, 21 February 2011
Inizio » Applicazioni » Istruzione » Step

|
Step è un simulatore fisico interattivo. Ti permette di esplorare il mondo della fisica tramite simulazioni. Fa parte del progetto KDE Education. |
Descrizione
Step è un simulatore fisico interattivo. Funziona così: posiziona alcuni corpi nella scena, aggiungi alcune forze come gravità o molle, poi fai clic su e Step ti mostrerà come la scena evolve secondo le leggi della fisica. Puoi modificare ogni proprietà dei corpi/forze nel tuo esperimento (anche durante la simulazione) e vedere come questo modificherà il risultato dell'esperimento. Con Step puoi non solo imparare, ma anche "sentire" come funziona la fisica!
Caratteristiche
- Classical mechanical simulation in two dimensions
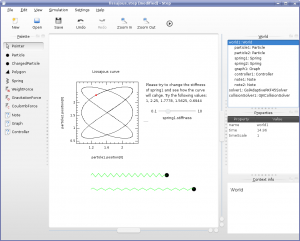
- Particles, springs with damping, gravitational and Coulomb forces
- Rigid bodies
- Collision detection (currently only discrete) and handling
- Soft (deformable) bodies simulated as user-editable particles-springs system, sound waves
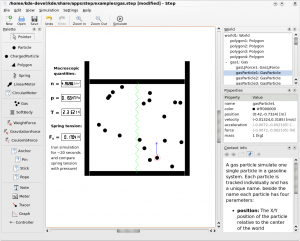
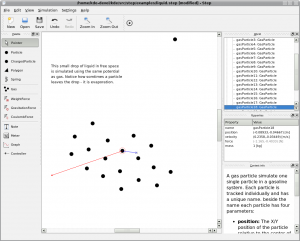
- Molecular dynamics (currently using Lennard-Jones potential): gas and liquid, condensation and evaporation, calculation of macroscopic quantities and their variances
- Units conversion and expression calculation: you can enter something like "(2 days + 3 hours) * 80 km/h" and it will be accepted as distance value (requires libqalculate)
- Errors calculation and propagation: you can enter values like "1.3 ± 0.2" for any property and errors for all dependent properties will be calculated using statistical formulas
- Solver error estimation: errors introduced by the solver is calculated and added to user-entered errors
- Several different solvers: up to 8th order, explicit and implicit, with or without adaptive timestep (most of the solvers require GSL library)
- Controller tool to easily control properties during simulation (even with custom keyboard shortcuts)
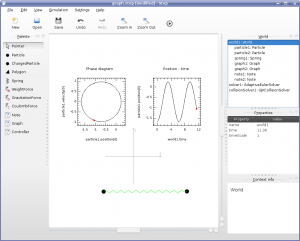
- Tools to visualize results: graph, meter, tracer
- Context information for all objects, integrated wikipedia browser
- Collection of example experiments, more can be downloaded with KNewStuff2
- Integrated tutorials
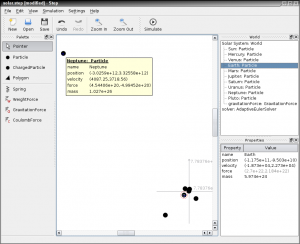
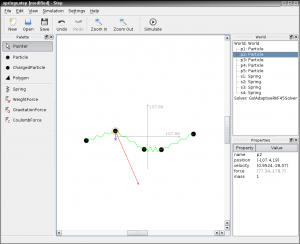
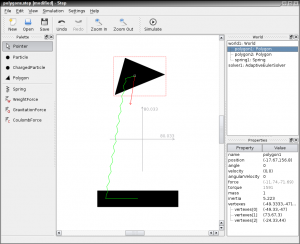
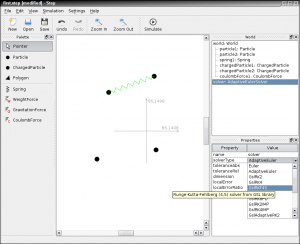
Screenshots
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Documentation
Weblinks
StepCore Library
StepCore is the physical simulation library on which Step is based. It can be used without Step for complex simulations which require coding or in other software which require physical simulation functionality. It is designed in order to be extensible, tunable and to provide accurate simulation.
You can find more information about the StepCore library on techbase.kde.org.
