System Activity: Difference between revisions
Appearance
No edit summary |
m Added links |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Although this is one of the | Although this is one of the [[KSysGuard]] modules, it is usefully available on demand, as a stand-alone. In KDE SC 4.3, this can only be accessed by the keyboard shortcut Ctrl-Esc or from the spanner (wrench) to the left in a [[KRunner]] (Alt-F2) window. A menu entry may follow. | ||
This is particularly useful when you have a misbehaving window, that refuses to close by normal methods. Simply highlight the process, then hit the Kill button. | This is particularly useful when you have a misbehaving window, that refuses to close by normal methods. Simply highlight the process, then hit the Kill button. | ||
Revision as of 09:09, 29 November 2009
Template:I18n/Language Navigation Bar
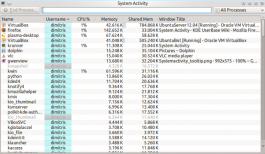 |
See your running processes listed |
Although this is one of the KSysGuard modules, it is usefully available on demand, as a stand-alone. In KDE SC 4.3, this can only be accessed by the keyboard shortcut Ctrl-Esc or from the spanner (wrench) to the left in a KRunner (Alt-F2) window. A menu entry may follow.
This is particularly useful when you have a misbehaving window, that refuses to close by normal methods. Simply highlight the process, then hit the Kill button.
You can, of course, choose between seeing All Processes, User-owned Processes, System Processes and Programmes Only. If you select All Processes, Tree, you can see whether anything else might be affected by killing your problem window.
