Configuration du système/Associations de fichiers
 |
Modifier un type de fichier existant, ou en créer un nouveau |
L'espace de travail et les applications individuelles connaissent les différents types de fichiers par leur type de fichier. C’est ce qui leur permet de gérer de manière appropriée les différents types de fichiers. Cette boîte de dialogue de paramètres vous permet de configurer la manière dont tout type de fichier connu doit être géré. Il vous permet également de définir de nouveaux types de fichiers ou de modifier la façon dont un type connu est reconnu.
Alternativement, vous pouvez configurer un type de fichier dans Dolphin en utilisant l'une des 3 méthodes pour modifier les associations de fichiers.
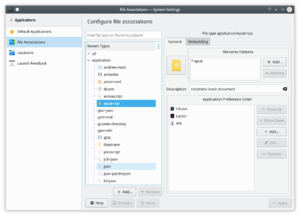
Configuration des types de fichiers connus
Dans la liste située dans la partie gauche de la fenêtre, vous trouverez un outil de recherche et une liste de tous les types de fichiers connus rassemblés dans un certain nombre de groupes. Pour rechercher un type de fichier, saisissez une partie de son nom de type de fichier ou de son modèle de nom de fichier dans la ligne de saisie en haut.
You can also browse the list of file types. Just expand the relevant category, and go through the list of file types that appear. Some of these list are very long, though.
To modify a file type, locate it in the list of file types and click on its name. Now you will see two tabs in the right side of the dialog.
In the tab you can change the icon associated with this type of file by clicking the icon button in the top left of the tab. You can add or remove file name patterns in the list, thereby defining which files are recognized as having this type. The list in the bottom part of the tab names the applications that will show up in the context menu, when you right click on a file of this type. The first application in the list is the one that is used when you left click on the file.
The options in the tab affect how the file type is handled by Konqueror, when it is used as a file manager.
Adding new file types locally
To add a new file type click on the button below the list of file types in the left side of the window. That brings up a dialog where you should select a group from the dropdown list and enter a name in the text field. Then click the button to create your new file type.
Now you can edit the new file type in exactly the same way that you modified an existing file type.
Requesting new file types
The KDE software guesses filetypes using the shared-mime-info database, which is shared with many other software projects. To request a new file type to be added to the database, please, follow the instructions here.


