KDevelop4/Manual/Running programs: Difference between revisions
Marked this version for translation |
m Formatting changes |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
<!--T:2--> | <!--T:2--> | ||
Once you have built a program, you will want to run it. To do this, need to configure | Once you have built a program, you will want to run it. To do this, need to configure ''Launches'' for your projects. A ''Launch'' consists of the name of an executable, a set of command line parameters, and an execution environment (such as "run this program in a shell", or "run this program in the debugger"). | ||
</translate><span id="Setting up launches in KDevelop"></span><translate> | </translate><span id="Setting up launches in KDevelop"></span><translate> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
<!--T:5--> | <!--T:5--> | ||
To set this up go to menu item <menuchoice>Run -> Configure launches</menuchoice>, highlight the project you want to add a launch for, and click on the | To set this up go to menu item <menuchoice>Run -> Configure launches</menuchoice>, highlight the project you want to add a launch for, and click on the {{Plus}} button. Then enter the name of the executable, and the path where you want to run the program. If running the executable depends on building the executable and/or other libraries first, then you may want to add them to the list at the bottom: select <menuchoice>Build</menuchoice> from the dropdown menu, then hit the folder symbol to the right of the textbox and select whatever target you want to have built. In the example above, I have selected the target <menuchoice>all</menuchoice> from project '''''1.deal.II''''' and '''''step-32''''' from project '''''1.step-32''''' to make sure both the base library and the application program have been compiled and are up to date before the program is actually executed. While you're there, you may as well also configure a debug launch by clicking on the <menuchoice>Debug</menuchoice> symbol and adding the name of the debugger program; if this is the system's default debugger (e.g. '''gdb''' on Linux), then you don't need to do this step. | ||
<!--T:6--> | <!--T:6--> | ||
Revision as of 04:57, 12 June 2011
Running programs in KDevelop
Once you have built a program, you will want to run it. To do this, need to configure Launches for your projects. A Launch consists of the name of an executable, a set of command line parameters, and an execution environment (such as "run this program in a shell", or "run this program in the debugger").
Setting up launches in KDevelop
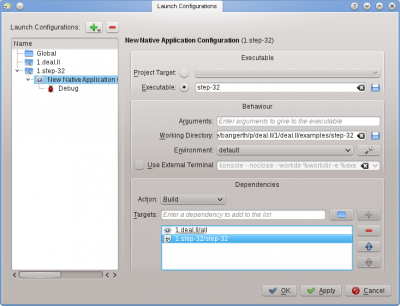
To set this up go to menu item , highlight the project you want to add a launch for, and click on the ![]() button. Then enter the name of the executable, and the path where you want to run the program. If running the executable depends on building the executable and/or other libraries first, then you may want to add them to the list at the bottom: select from the dropdown menu, then hit the folder symbol to the right of the textbox and select whatever target you want to have built. In the example above, I have selected the target from project 1.deal.II and step-32 from project 1.step-32 to make sure both the base library and the application program have been compiled and are up to date before the program is actually executed. While you're there, you may as well also configure a debug launch by clicking on the symbol and adding the name of the debugger program; if this is the system's default debugger (e.g. gdb on Linux), then you don't need to do this step.
button. Then enter the name of the executable, and the path where you want to run the program. If running the executable depends on building the executable and/or other libraries first, then you may want to add them to the list at the bottom: select from the dropdown menu, then hit the folder symbol to the right of the textbox and select whatever target you want to have built. In the example above, I have selected the target from project 1.deal.II and step-32 from project 1.step-32 to make sure both the base library and the application program have been compiled and are up to date before the program is actually executed. While you're there, you may as well also configure a debug launch by clicking on the symbol and adding the name of the debugger program; if this is the system's default debugger (e.g. gdb on Linux), then you don't need to do this step.
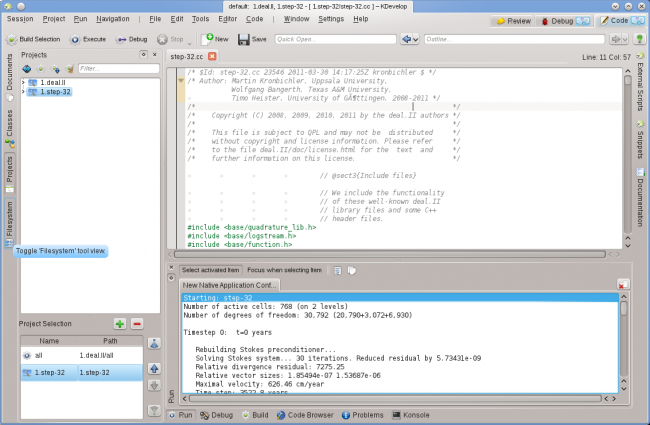
You can now try to run the program: Select from KDevelop's main window menu (or hit Shift + F9) and your program should run in a separate subwindow of KDevelop. The picture above shows the result: The new tool subwindow at the bottom shows the output of the program that is being run, in this case of the step-32 program.
Some useful keyboard shortcuts
| Running a program | |
|---|---|
| F8 | Build (call make) |
| Shift + F9 | Run |
| F9 | Run program in the debugger; you may want to set breakpoints beforehand, for example by right-clicking with the mouse on a particular line in the source code |

