KSysGuard/zh-cn: Difference between revisions
m Created page with "==概述==" |
Updating to match new version of source page |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|[[Image:Ksysguard1.png|thumb|265px|系统负载]]|| '''追踪控制系统进程.''' | |[[Image:Ksysguard1.png|thumb|265px|系统负载]]|| '''追踪控制系统进程.''' | ||
|} | |} | ||
<span id="General"></span> | |||
==概述== | ==概述== | ||
''' | '''系统监视器(KSysGuard)''',即'''KDE 系统监视器''',设计简单,无需特别设置即可进行简单的进程控制 - 通常默认设置就够用了。它包含两张工作表 - <menuchoice>系统负载</menuchoice>(上面是图表)和<menuchoice>进程表</menuchoice>。 | ||
You can also download other tabs (File >> Download New Tabs), including temperatures, network and more. | |||
<span id="System_Load"></span> | |||
==系统负载== | |||
<menuchoice>系统负载</menuchoice>屏有3个显示图表,每个分别描绘如下负载要素 - 「CPU历史」,「内存和交换文件空间历史」,「网络历史」。如果你悬停鼠标指针到每个部分的,你会看到带有颜色的详细分析。 | |||
{|class="tablecenter" | {|class="tablecenter" | ||
| Line 20: | Line 24: | ||
|} | |} | ||
== | <span id="The_Process_Table"></span> | ||
==进程表== | |||
默认的<menuchoice>全部进程</menuchoice>视图会给你一份按照字母排序的所有运行的程序列表。点击任何列的标题会以此列排序。如果你有一个runaway进程(这种进程陷入无限循环,不停派生出子进程),你会发现<menuchoice>全部进程, 树形</menuchoice>视图最有用。你也能选择用「拥有者」或「程序」查看进程的子集。 | |||
{|class="tablecenter" | {|class="tablecenter" | ||
|[[Image:Ksysguard2.png|thumb|300px| | |[[Image:Ksysguard2.png|thumb|300px|进程字母排序]]||[[Image:KsysguardTree.png|thumb|300px| 树形视图]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
== | <span id="Hints_and_Tips"></span> | ||
==提示和技巧== | |||
<keycap>Ctrl+Esc</keycap> 能启动系统监视器的''进程''模块,通常在你想找出哪个程序占用太多资源的时候非常有用。 | |||
<keycap> | <div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | ||
在 [[Special:myLanguage/KRunner|KRunner]] (<keycap>Alt-F2 </keycap>或是右击桌面) 上位于输入框左侧有个小图标-它看起来像微波炉-也能启动进程表。 | |||
</div> | |||
'''Editing Tabs''': Should you want to adjust a tab, you can find the corresponding .sgrd-file in ~/.local/share/ksysguard/. Once you set "locked" to 0, the sensor browser becomes visible after restarting ksysguard. Now you can drag any sensor from the right into any graph on the left. Setting "locked" back to 1 disables the window again. | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:系统/zh-cn]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:30, 10 August 2023
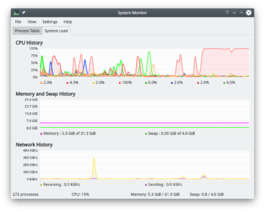 |
追踪控制系统进程. |
概述
系统监视器(KSysGuard),即KDE 系统监视器,设计简单,无需特别设置即可进行简单的进程控制 - 通常默认设置就够用了。它包含两张工作表 - (上面是图表)和。
You can also download other tabs (File >> Download New Tabs), including temperatures, network and more.
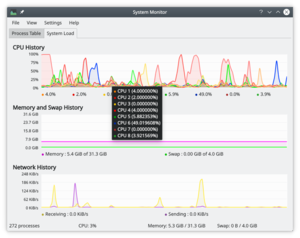
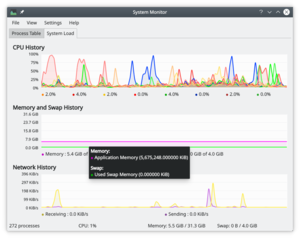
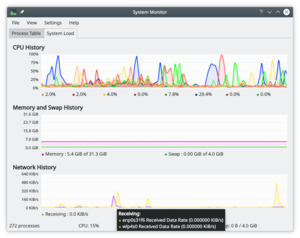
系统负载
屏有3个显示图表,每个分别描绘如下负载要素 - 「CPU历史」,「内存和交换文件空间历史」,「网络历史」。如果你悬停鼠标指针到每个部分的,你会看到带有颜色的详细分析。
 |
 |
 |
进程表
默认的视图会给你一份按照字母排序的所有运行的程序列表。点击任何列的标题会以此列排序。如果你有一个runaway进程(这种进程陷入无限循环,不停派生出子进程),你会发现视图最有用。你也能选择用「拥有者」或「程序」查看进程的子集。
 |
 |
提示和技巧
Ctrl+Esc 能启动系统监视器的进程模块,通常在你想找出哪个程序占用太多资源的时候非常有用。
在 KRunner (Alt-F2 或是右击桌面) 上位于输入框左侧有个小图标-它看起来像微波炉-也能启动进程表。
Editing Tabs: Should you want to adjust a tab, you can find the corresponding .sgrd-file in ~/.local/share/ksysguard/. Once you set "locked" to 0, the sensor browser becomes visible after restarting ksysguard. Now you can drag any sensor from the right into any graph on the left. Setting "locked" back to 1 disables the window again.
